Effects of Prolonged GRP78 Haploinsufficiency on Organ Homeostasis, Behavior, Cancer and Chemotoxic Resistance in Aged Mice
- PMID: 28145503
- PMCID: PMC5286507
- DOI: 10.1038/srep40919
Effects of Prolonged GRP78 Haploinsufficiency on Organ Homeostasis, Behavior, Cancer and Chemotoxic Resistance in Aged Mice
Abstract
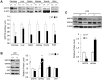
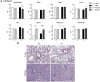
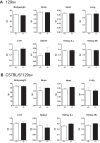
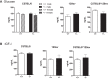
GRP78, a multifunctional protein with potent cytoprotective properties, is an emerging therapeutic target to combat cancer development, progression and drug resistance. The biological consequences of prolonged reduction in expression of this essential chaperone which so far has been studied primarily in young mice, was investigated in older mice, as older individuals are likely to be important recipients of anti-GRP78 therapy. We followed cohorts of Grp78+/+ and Grp78+/- male and female mice up to 2 years of age in three different genetic backgrounds and characterized them with respect to body weight, organ integrity, behavioral and memory performance, cancer, inflammation and chemotoxic response. Our results reveal that body weight, organ development and integrity were not impaired in aged Grp78+/- mice. No significant effect on cancer incidence and inflammation was observed in aging mice. Interestingly, our studies detected some subtle differential trends between the WT and Grp78+/- mice in some test parameters dependent on gender and genetic background. Our studies provide the first evidence that GRP78 haploinsufficiency for up to 2 years of age has no major deleterious effect in rodents of different genetic background, supporting the merit of anti-GRP78 drugs in treatment of cancer and other diseases affecting the elderly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GRP78 haploinsufficiency suppresses acinar-to-ductal metaplasia, signaling, and mutant Kras-driven pancreatic tumorigenesis in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 May 16;114(20):E4020-E4029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1616060114. Epub 2017 May 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28461470 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress-mediated aldehyde adduction of GRP78 in a mouse model of alcoholic liver disease: functional independence of ATPase activity and chaperone function.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Aug;73:411-20. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 24924946 Free PMC article.
-
The loss of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) during normal aging or from siRNA knockdown augments human alpha-synuclein (α-syn) toxicity to rat nigral neurons.Neurobiol Aging. 2015 Jun;36(6):2213-23. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.02.018. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Neurobiol Aging. 2015. PMID: 25863526 Free PMC article.
-
The Glucose-Regulated Protein78 (GRP78) in the Unfolded Protein Response (UPR) Pathway: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Breast Cancer.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2023;23(5):505-524. doi: 10.2174/1871520622666220823094350. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36017846 Review.
-
Cell surface GRP78 signaling: An emerging role as a transcriptional modulator in cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Apr;236(4):2352-2363. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30030. Epub 2020 Aug 31. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 32864780 Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of stress induction of the 78-kilodalton glucose regulated protein (GRP78) in cancer by IT-139, an anti-tumor ruthenium small molecule inhibitor.Oncotarget. 2018 Jul 3;9(51):29698-29714. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25679. eCollection 2018 Jul 3. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30038714 Free PMC article.
-
GRP78 haploinsufficiency suppresses acinar-to-ductal metaplasia, signaling, and mutant Kras-driven pancreatic tumorigenesis in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 May 16;114(20):E4020-E4029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1616060114. Epub 2017 May 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28461470 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-induced translocation of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone GRP78/BiP and its impact on human disease and therapy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jul 29;122(30):e2412246122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2412246122. Epub 2025 Jul 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40699920 Free PMC article.
-
BiP/GRP78 is a pro-viral factor for diverse dsDNA viruses that promotes the survival and proliferation of cells upon KSHV infection.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Oct 29;20(10):e1012660. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012660. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39471213 Free PMC article.
-
The stress-inducible ER chaperone GRP78/BiP is upregulated during SARS-CoV-2 infection and acts as a pro-viral protein.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 14;13(1):6551. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34065-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36376289 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ma Y. & Hendershot L. M. The role of the unfolded protein response in tumour development: friend or foe? Nat. Rev. Cancer 4, 966–977 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

