A cocktail of three virulent bacteriophages prevents Vibrio cholerae infection in animal models
- PMID: 28146150
- PMCID: PMC5296635
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14187
A cocktail of three virulent bacteriophages prevents Vibrio cholerae infection in animal models
Abstract
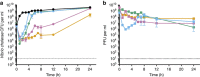
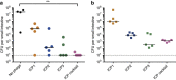
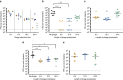
Effective prevention strategies will be essential in reducing disease burden due to bacterial infections. Here we harness the specificity and rapid-acting properties of bacteriophages as a potential prophylaxis therapy for cholera, a severely dehydrating disease caused by Vibrio cholerae. To this end, we test a cocktail of three virulent phages in two animal models of cholera pathogenesis (infant mouse and rabbit models). Oral administration of the phages up to 24 h before V. cholerae challenge reduces colonization of the intestinal tract and prevents cholera-like diarrhea. None of the surviving V. cholerae colonies are resistant to all three phages. Genome sequencing and variant analysis of the surviving colonies indicate that resistance to the phages is largely conferred by mutations in genes required for the production of the phage receptors. For acute infections, such as cholera, phage prophylaxis could provide a strategy to limit the impact of bacterial disease on human health.
Conflict of interest statement
M.Y., L.S.C. and A.C. have filed a provisional application, application number 62-316704, with the US Patent and Trademark Office on this work.
Figures

References
-
- Zuckerman J. N., Rombo L. & Fisch A. The true burden and risk of cholera: implications for prevention and control. Lancet Infect. Dis. 7, 521–530 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Bagcchi S. Cholera in Iraq strains the fragile state. Lancet Infect. Dis. 16, 24–25 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Qadri F. et al.. Efficacy of a single-dose, inactivated oral cholera vaccine in Bangladesh. N. Engl. J. Med. 374, 1723–1732 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

