Rare and low-frequency coding variants alter human adult height
- PMID: 28146470
- PMCID: PMC5302847
- DOI: 10.1038/nature21039
Rare and low-frequency coding variants alter human adult height
Abstract
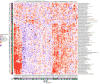
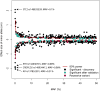
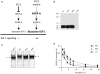
Height is a highly heritable, classic polygenic trait with approximately 700 common associated variants identified through genome-wide association studies so far. Here, we report 83 height-associated coding variants with lower minor-allele frequencies (in the range of 0.1-4.8%) and effects of up to 2 centimetres per allele (such as those in IHH, STC2, AR and CRISPLD2), greater than ten times the average effect of common variants. In functional follow-up studies, rare height-increasing alleles of STC2 (giving an increase of 1-2 centimetres per allele) compromised proteolytic inhibition of PAPP-A and increased cleavage of IGFBP-4 in vitro, resulting in higher bioavailability of insulin-like growth factors. These 83 height-associated variants overlap genes that are mutated in monogenic growth disorders and highlight new biological candidates (such as ADAMTS3, IL11RA and NOX4) and pathways (such as proteoglycan and glycosaminoglycan synthesis) involved in growth. Our results demonstrate that sufficiently large sample sizes can uncover rare and low-frequency variants of moderate-to-large effect associated with polygenic human phenotypes, and that these variants implicate relevant genes and pathways.
Figures

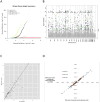

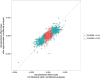
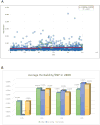
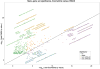


Comment in
-
Genetics: Unlocking the secrets of adult human height.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017 Apr;13(4):190. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.20. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28211515 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fisher RA. The Correlation Between Relatives on the Supposition of Mendelian Inheritance. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 1918;52:399–433.
-
- Silventoinen K, et al. Heritability of adult body height: a comparative study of twin cohorts in eight countries. Twin Res. 2003;6:399–408. - PubMed
-
- Steinthorsdottir V, et al. Identification of low-frequency and rare sequence variants associated with elevated or reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2014;46:294–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K99 HL130580/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DP3 DK108220/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12013/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL127564/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M501633/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K006584/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/F019394/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- K23 HL114724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007417/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK106621/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K002414/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 HG008657/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- SP/13/2/30111/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 068545/Z/02/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0700931/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/08/014/24067/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- KL2 TR001109/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100046C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L01632X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R35 HL135824/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK075787/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY022310/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L01341X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K026992/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L003120/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- S10 OD018522/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- G0601966/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL119443/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_15018/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- UM1 CA182913/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM096911/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK107904/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089256/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0700704/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/14/5/30893/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MR/K007017/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201300046C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD057194/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_13040/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL117078/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 2014105/DDCF/Doris Duke Charitable Foundation/United States
- P2C HD050924/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 202802/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- T32 HL007055/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0600237/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HC095159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G9815508/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH090553/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M501633/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

