Selective expansion of high functional avidity memory CD8 T cell clonotypes during hepatitis C virus reinfection and clearance
- PMID: 28146579
- PMCID: PMC5305272
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006191
Selective expansion of high functional avidity memory CD8 T cell clonotypes during hepatitis C virus reinfection and clearance
Abstract
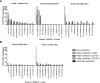
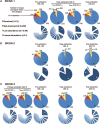
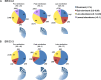
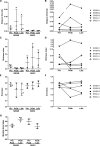
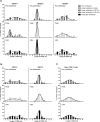
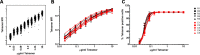
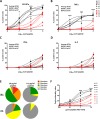
The dynamics of the memory CD8 T cell receptor (TCR) repertoire upon virus re-exposure and factors governing the selection of TCR clonotypes conferring protective immunity in real life settings are poorly understood. Here, we examined the dynamics and functionality of the virus-specific memory CD8 TCR repertoire before, during and after hepatitis C virus (HCV) reinfection in patients who spontaneously resolved two consecutive infections (SR/SR) and patients who resolved a primary but failed to clear a subsequent infection (SR/CI). The TCR repertoire was narrower prior to reinfection in the SR/SR group as compared to the SR/CI group and became more focused upon reinfection. CD8 T cell clonotypes expanding upon re-exposure and associated with protection from viral persistence were recruited from the memory T cell pool. Individual CD8 T cell lines generated from the SR/SR group exhibited higher functional avidity and polyfunctionality as compared to cell lines from the SR/CI group. Our results suggest that protection from viral persistence upon HCV reinfection is associated with focusing of the HCV-specific CD8 memory T cell repertoire from which established cell lines showed high functional avidity. These findings are applicable to vaccination strategies aiming at shaping the protective human T cell repertoire.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Venturi V, Price DA, Douek DC, Davenport MP. The molecular basis for public T-cell responses? Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(3):231–8. http://www.nature.com/nri/journal/v8/n3/suppinfo/nri2260_S1.html. 10.1038/nri2260 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

