Visualizing Changes in Cdkn1c Expression Links Early-Life Adversity to Imprint Mis-regulation in Adults
- PMID: 28147266
- PMCID: PMC5300902
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.010
Visualizing Changes in Cdkn1c Expression Links Early-Life Adversity to Imprint Mis-regulation in Adults
Abstract
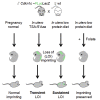
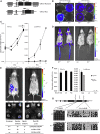
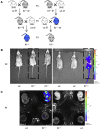
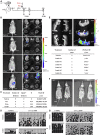
Imprinted genes are regulated according to parental origin and can influence embryonic growth and metabolism and confer disease susceptibility. Here, we designed sensitive allele-specific reporters to non-invasively monitor imprinted Cdkn1c expression in mice and showed that expression was modulated by environmental factors encountered in utero. Acute exposure to chromatin-modifying drugs resulted in de-repression of paternally inherited (silent) Cdkn1c alleles in embryos that was temporary and resolved after birth. In contrast, deprivation of maternal dietary protein in utero provoked permanent de-repression of imprinted Cdkn1c expression that was sustained into adulthood and occurred through a folate-dependent mechanism of DNA methylation loss. Given the function of imprinted genes in regulating behavior and metabolic processes in adults, these results establish imprinting deregulation as a credible mechanism linking early-life adversity to later-life outcomes. Furthermore, Cdkn1c-luciferase mice offer non-invasive tools to identify factors that disrupt epigenetic processes and strategies to limit their long-term impact.
Keywords: Cdkn1c; bioluminescence; environmental stress; imprinting; luciferase reporter mice.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bhogal B., Arnaudo A., Dymkowski A., Best A., Davis T.L. Methylation at mouse Cdkn1c is acquired during postimplantation development and functions to maintain imprinted expression. Genomics. 2004;84:961–970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/M013960/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 095606/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_U120027516/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U120085816/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J015156 /BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

