Oncogenic mechanisms of Lin28 in breast cancer: new functions and therapeutic opportunities
- PMID: 28147339
- PMCID: PMC5421965
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14891
Oncogenic mechanisms of Lin28 in breast cancer: new functions and therapeutic opportunities
Abstract
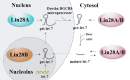
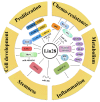
The RNA binding protein Lin28 is best known for the critical role in cell development, recent researches also have implied its oncogenic function in various human cancers, including breast cancer. Specifically, aberrant Lin28 participates in multiple pathological processes, such as proliferation, metastasis, radiotherapy and chemotherapy resistance, metabolism, immunity and inflammation as well as stemness. In this review, we summarize the let-7-dependent and let-7-independent mechanism regulated by Lin28, focusing on its relation with tumor hallmarks in breast cancer, and subsequently discuss our present knowledge of Lin28 to develop a molecular-based therapeutic strategy against breast cancer.
Keywords: Let-7; Lin28; breast cancer; drug resistance; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed. None of the contents of this manuscript has been previously published or is under consideration elsewhere. All the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript prior to submission.
Figures


References
-
- Licznerska B, Baer-Dubowska W. Estrogen intracrinology: therapy and chemoprevention of breast cancer. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online) 2010;64:220–30. - PubMed
-
- Moss EG, Lee RC, Ambros V. The cold shock domain protein LIN-28 controls developmental timing in C. elegans and is regulated by the lin-4 RNA. Cell. 1997;88:637–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

