Inhibition of CDK8 mediator kinase suppresses estrogen dependent transcription and the growth of estrogen receptor positive breast cancer
- PMID: 28147342
- PMCID: PMC5355036
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14894
Inhibition of CDK8 mediator kinase suppresses estrogen dependent transcription and the growth of estrogen receptor positive breast cancer
Abstract
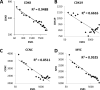
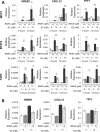
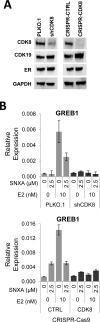
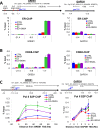
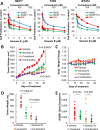
Hormone therapy targeting estrogen receptor (ER) is the principal treatment for ER-positive breast cancers. However, many cancers develop resistance to hormone therapy while retaining ER expression. Identifying new druggable mediators of ER function can help to increase the efficacy of ER-targeting drugs. Cyclin-dependent kinase 8 (CDK8) is a Mediator complex-associated transcriptional regulator with oncogenic activities. Expression of CDK8, its paralog CDK19 and their binding partner Cyclin C are negative prognostic markers in breast cancer. Meta-analysis of transcriptome databases revealed an inverse correlation between CDK8 and ERα expression, suggesting that CDK8 could be functionally associated with ER. We have found that CDK8 inhibition by CDK8/19-selective small-molecule kinase inhibitors, by shRNA knockdown or by CRISPR/CAS9 knockout suppresses estrogen-induced transcription in ER-positive breast cancer cells; this effect was exerted downstream of ER. Estrogen addition stimulated the binding of CDK8 to the ER-responsive GREB1 gene promoter and CDK8/19 inhibition reduced estrogen-stimulated association of an elongation-competent phosphorylated form of RNA Polymerase II with GREB1. CDK8/19 inhibitors abrogated the mitogenic effect of estrogen on ER-positive cells and potentiated the growth-inhibitory effects of ER antagonist fulvestrant. Treatment of estrogen-deprived ER-positive breast cancer cells with CDK8/19 inhibitors strongly impeded the development of estrogen independence. In vivo treatment with a CDK8/19 inhibitor Senexin B suppressed tumor growth and augmented the effects of fulvestrant in ER-positive breast cancer xenografts. These results identify CDK8 as a novel downstream mediator of ER and suggest the utility of CDK8 inhibitors for ER-positive breast cancer therapy.
Keywords: CDK8; breast cancer; estrogen independence; estrogen receptor; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
EVB is a consultant, MC is a contract PI and a consultant and IBR is the President of Senex Biotechnology, Inc.
Figures




Comment in
-
CDK8: a new breast cancer target.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 28;8(9):14269-14270. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15354. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28209918 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- The American Cancer Society What are the key statistics about breast cancer? 2016
-
- Clark GM, Osborne CK, McGuire WL. Correlations between estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and patient characteristics in human breast cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 1984;2:1102–1109. - PubMed
-
- Keen JC, Davidson NE. The biology of breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2003;97:825–833. - PubMed
-
- Lim E, Metzger-Filho O, Winer EP. The natural history of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Oncology (Williston Park, N.Y.) 2012;26:688–94. 696. - PubMed
-
- Tsai MJ, O'Malley BW. Molecular mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily members. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 1994;63:451–486. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

