The ribosomal protein gene RPL5 is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor in multiple cancer types
- PMID: 28147343
- PMCID: PMC5362418
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14895
The ribosomal protein gene RPL5 is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor in multiple cancer types
Abstract
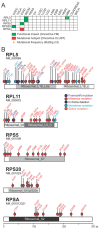
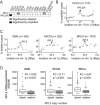
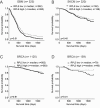
For many years, defects in the ribosome have been associated to cancer. Recently, somatic mutations and deletions affecting ribosomal protein genes were identified in a few leukemias and solid tumor types. However, systematic analysis of all 81 known ribosomal protein genes across cancer types is lacking. We screened mutation and copy number data of respectively 4926 and 7322 samples from 16 cancer types and identified six altered genes (RPL5, RPL11, RPL23A, RPS5, RPS20 and RPSA). RPL5 was located at a significant peak of heterozygous deletion or mutated in 11% of glioblastoma, 28% of melanoma and 34% of breast cancer samples. Moreover, patients with low RPL5 expression displayed worse overall survival in glioblastoma and in one breast cancer cohort. RPL5 knockdown in breast cancer cell lines enhanced G2/M cell cycle progression and accelerated tumor progression in a xenograft mouse model. Interestingly, our data suggest that the tumor suppressor role of RPL5 is not only mediated by its known function as TP53 or c-MYC regulator. In conclusion, RPL5 heterozygous inactivation occurs at high incidence (11-34%) in multiple tumor types, currently representing the most common somatic ribosomal protein defect in cancer, and we demonstrate a tumor suppressor role for RPL5 in breast cancer.
Keywords: TCGA; breast cancer; haploinsufficient tumor suppressor; ribosomal protein.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- De Keersmaecker K, Atak ZK, Li N, Vicente C, Patchett S, Girardi T, Gianfelici V, Geerdens E, Clappier E, Porcu M, Lahortiga I, Lucà R, Yan J, et al. Exome sequencing identifies mutation in CNOT3 and ribosomal genes RPL5 and RPL10 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Genet. 2013;45:186–90. doi: 10.1038/ng.2508. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rao S, Lee SY, Gutierrez A, Perrigoue J, Thapa RJ, Tu Z, Jeffers JR, Rhodes M, Anderson S, Oravecz T, Hunger SP, Timakhov RA, Zhang R, et al. Inactivation of ribosomal protein L22 promotes transformation by induction of the stemness factor, Lin28B. Blood. 2012;120:3764–73. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-03-415349. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tzoneva G, Perez-Garcia A, Carpenter Z, Khiabanian H, Tosello V, Allegretta M, Paietta E, Racevskis J, Rowe JM, Tallman MS, Paganin M, Basso G, Hof J, et al. Activating mutations in the NT5C2 nucleotidase gene drive chemotherapy resistance in relapsed ALL. Nat Med. 2013;19:368–71. doi: 10.1038/nm.3078. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ljungström V, Cortese D, Young E, Pandzic T, Mansouri L, Plevova K, Ntoufa S, Baliakas P, Clifford R, Sutton LA, Blakemore SJ, Stavroyianni N, Agathangelidis A, et al. Whole-exome sequencing in relapsing chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Clinical impact of recurrent RPS15 mutations. Blood. 2016;127:1007–16. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-10-674572. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

