Detailed analysis of c-di-GMP mediated regulation of csgD expression in Salmonella typhimurium
- PMID: 28148244
- PMCID: PMC5289004
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-017-0934-5
Detailed analysis of c-di-GMP mediated regulation of csgD expression in Salmonella typhimurium
Abstract
Background: The secondary messenger cyclic di-GMP promotes biofilm formation by up regulating the expression of csgD, encoding the major regulator of rdar biofilm formation in Salmonella typhimurium. The GGDEF/EAL domain proteins regulate the c-di-GMP turnover. There are twenty- two GGDEF/EAL domain proteins in the genome of S. typhimurium. In this study, we dissect the role of individual GGDEF/EAL proteins for csgD expression and rdar biofilm development.
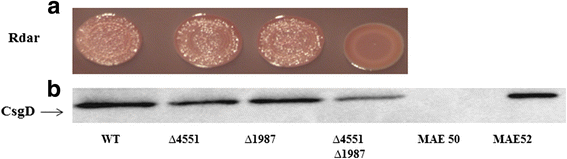
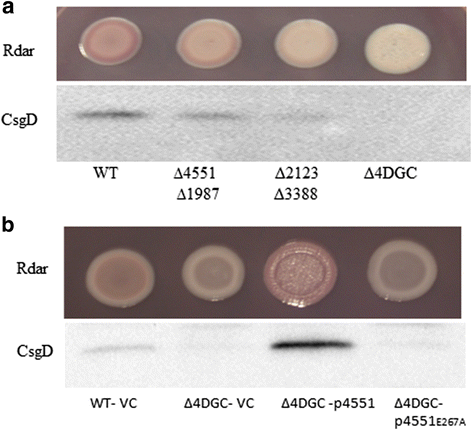
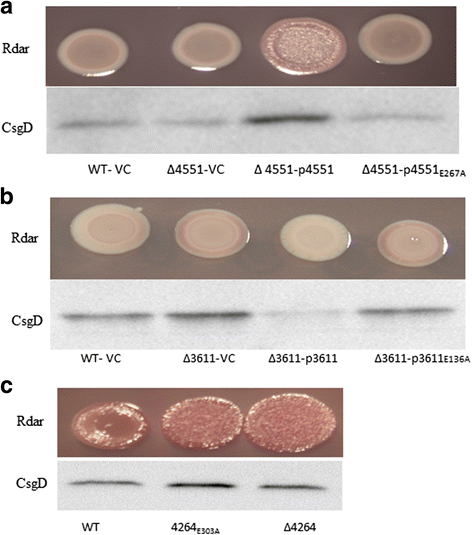
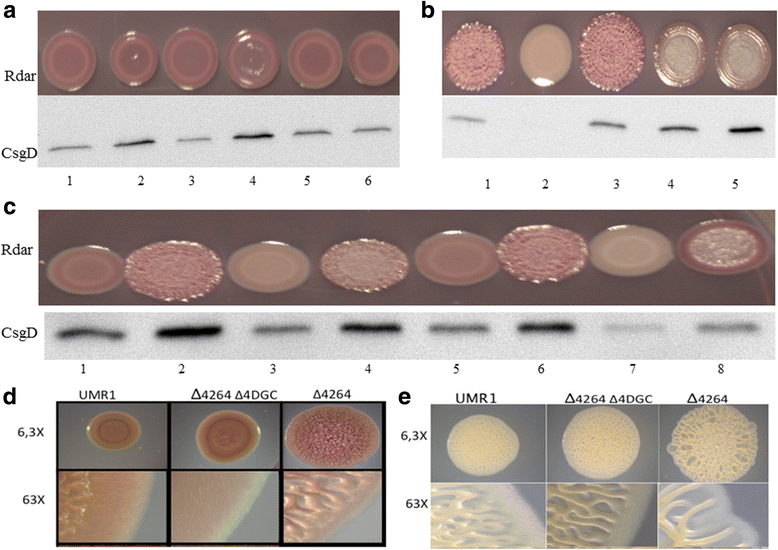
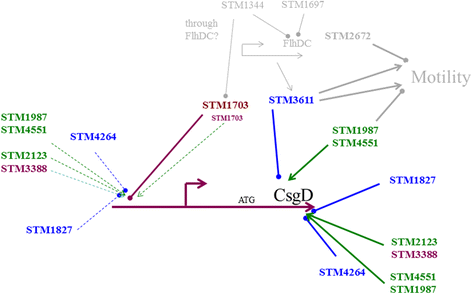
Results: Among twelve GGDEF domains, two proteins upregulate and among fifteen EAL domains, four proteins down regulate csgD expression. We identified two additional GGDEF proteins required to promote optimal csgD expression. With the exception of the EAL domain of STM1703, solely, diguanylate cyclase and phosphodiesterase activities are required to regulate csgD mediated rdar biofilm formation. Identification of corresponding phosphodiesterases and diguanylate cyclases interacting in the csgD regulatory network indicates various levels of regulation by c-di-GMP. The phosphodiesterase STM1703 represses transcription of csgD via a distinct promoter upstream region.
Conclusion: The enzymatic activity and the protein scaffold of GGDEF/EAL domain proteins regulate csgD expression. Thereby, c-di-GMP adjusts csgD expression at multiple levels presumably using a multitude of input signals.
Keywords: CsgD; GGDEF/EAL domain proteins; Salmonella typhimurium; biofilm formation; c-di-GMP; rdar morphotype.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A role for the EAL-like protein STM1344 in regulation of CsgD expression and motility in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2009 Jun;191(12):3928-37. doi: 10.1128/JB.00290-09. Epub 2009 Apr 17. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19376870 Free PMC article.
-
Role of EAL-containing proteins in multicellular behavior of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2007 May;189(9):3613-23. doi: 10.1128/JB.01719-06. Epub 2007 Feb 23. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17322315 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of biofilm-formation in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium by the periplasmic DsbA/DsbB oxidoreductase system requires the GGDEF-EAL domain protein STM3615.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 25;9(8):e106095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106095. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25153529 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the rdar morphotype, a multicellular behaviour in Enterobacteriaceae.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005 Jun;62(11):1234-46. doi: 10.1007/s00018-005-4557-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 15818467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensing the messenger: the diverse ways that bacteria signal through c-di-GMP.Protein Sci. 2012 Jul;21(7):929-48. doi: 10.1002/pro.2093. Epub 2012 Jun 5. Protein Sci. 2012. PMID: 22593024 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclic-di-GMP regulation of virulence in bacterial pathogens.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2018 Jan;9(1):10.1002/wrna.1454. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1454. Epub 2017 Oct 8. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2018. PMID: 28990312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitrate Is an Environmental Cue in the Gut for Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Biofilm Dispersal through Curli Repression and Flagellum Activation via Cyclic-di-GMP Signaling.mBio. 2021 Feb 22;13(1):e0288621. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02886-21. Epub 2022 Feb 8. mBio. 2021. PMID: 35130730 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular glutamine fluctuates with nitrogen availability and regulates Mycobacterium smegmatis biofilm formation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 19:2025.06.18.660496. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.18.660496. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40666857 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
From Input to Output: The Lap/c-di-GMP Biofilm Regulatory Circuit.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2020 Sep 8;74:607-631. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-011520-094214. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32689917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of both anaerobic regulator genes fnr and narL compromises the colonization of Salmonella Typhimurium in mice model.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Nov 2;40(12):373. doi: 10.1007/s11274-024-04179-5. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39487264
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

