Enablers and barriers to evidence based planning in the district health system in Uganda; perceptions of district health managers
- PMID: 28148251
- PMCID: PMC5289024
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-017-2059-9
Enablers and barriers to evidence based planning in the district health system in Uganda; perceptions of district health managers
Abstract
Background: The District Health System was endorsed as the key strategy to achieve 'Health for all' during the WHO organized inter-regional meeting in Harare in 1987. Many expectations were put upon the district health system, including planning. Although planning should be evidence based to prioritize activities, in Uganda it has been described as occurring more by chance than by choice. The role of planning is entrusted to the district health managers with support from the Ministry of Health and other stakeholders, but there is limited knowledge on the district health manager's capacity to carry out evidence-based planning. The aim of this study was to determine the barriers and enablers to evidence-based planning at the district level.
Methods: This qualitative study collected data through key informant interviews with district managers from two purposefully selected districts in Uganda that have been implementing evidence-based planning. A deductive process of thematic analysis was used to classify responses within themes.
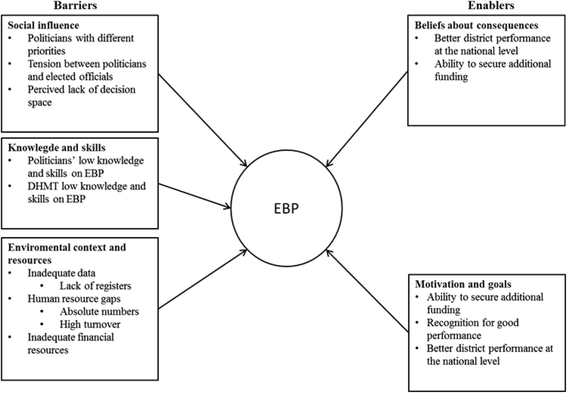
Results: There were considerable differences between the districts in regard to the barriers and enablers for evidence-based planning. Variations could be attributed to specific contextual and environmental differences such as human resource levels, date of establishment of the district, funding and the sociopolitical environment. The perceived lack of local decision space coupled with the perception that the politicians had all the power while having limited knowledge on evidence-based planning was considered an important barrier.
Conclusion: There is a need to review the mandate of the district managers to make decisions in the planning process and the range of decision space available within the district health system. Given the important role elected officials play in a decentralized system a concerted effort should be made to increase their knowledge on evidence-based planning and the district health system as a whole.
Keywords: Decentralization; District; Evidence; Health systems; Managers; Planning; Politicians; Uganda.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . Declaration on strengthening district health systems based on primary health care. Interregional meeting on strengthening district health systems. Harare: World Health Organization; 1987.
-
- World Bank . World Development Report: making services work for poor people. Washington D.C: World Bank; 2004.
-
- WHO . The World Health Report 2008: primary health care now more than ever. Geneva: WHO; 2008.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources