Potency and selectivity indices of acetone leaf extracts of nine selected South African trees against six opportunistic Enterobacteriaceae isolates from commercial chicken eggs
- PMID: 28148263
- PMCID: PMC5289020
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1597-3
Potency and selectivity indices of acetone leaf extracts of nine selected South African trees against six opportunistic Enterobacteriaceae isolates from commercial chicken eggs
Abstract
Background: The rise in antimicrobial resistance in a plethora of nosocomial and opportunistic bacterial pathogens often isolated from commercial eggs, poses a serious public health concern. The existence of these contaminants may also serve as a drawback in the current efforts of improving the well-being of immunocompromised patients. The aim of this study was to determine the efficacy of plant extracts that had good activity on Escherichia coli in previous word on pathogens isolated from eggs for possible use in combating pathogens from eggs.
Methods: Acetone leaf extracts of nine trees with good activities against Escherichia coli were tested for their in vitro antibacterial activity against six opportunistic bacterial isolates from commercial eggs (Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Salmonella serotype Typhimurium, Proteus mirabilis, Enterobacter cloacae and Escherichia coli) using a serial microdilution method with tetrazolium violet as indicator of growth. Cytotoxicity was determined using a tetrazolium-based colorimetric assay against Vero kidney cells, and selectivity index calculated.
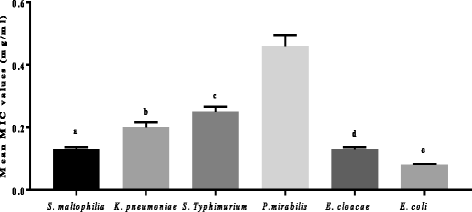
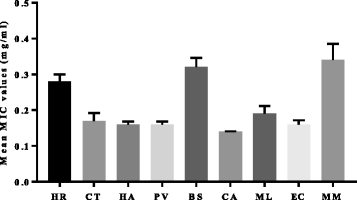
Results: The MIC values range of the different extracts against Stenotrophomonas maltophilia was 0.08-0.31 mg/ml, Klebsiella pneumonia 0.08-0.63 mg/ml, Salmonella ser. Typhimurium 0.08-0.63 mg/ml, Proteus mirabilis 0.02-1.25 mg/ml, Enterobacter cloacae 0.08-0.31 mg/ml and Escherichia coli 0.08-0.16 mg/ml respectively. Escherichia coli was the most sensitive while Proteus mirabilis was most resistant pathogen to the different test extracts, with mean MIC values of 0.08 mg/ml and 0.46 mg/ml respectively. Cremaspora triflora extracts had good activity against all the pathogenic egg isolates, with the exception of Proteus mirabilis. Maesa lanceolata and Elaeodendron croceum had the best total antibacterial activity (TAA), while generally the selectivity index of the extract was low (SI < 1).
Conclusion: The exceptional activity of C. triflora extracts suggests that the plant has potential as a therapeutic agent against some members of the Enterobacteriaceae. Further pharmacological investigations may be interesting in the search for new antimicrobial leads.
Keywords: Antimicrobial; Hens’ egg isolates; Nosocomial; Opportunistic pathogens; Plant extracts.
Figures
References
-
- Adesiyun A, Offiah N, Seepersadsingh N, Rodrigo S, Lashley V, Musai L. Frequency and antimicrobial resistance of enteric bacteria with spoilage potential isolated from table eggs. Food Res Int. 2006;39:212–219. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2005.07.008. - DOI
-
- Jambalang AR. The development and validation of a bacteriological screening test for antimicrobial residues in eggs. MSc Dissertation. South Africa: University of Pretoria; 2011. http://hdl.handle.net/2263/24843.
-
- Al-Ashmawy MA. Prevalence of Enterobacteriaceae in table eggs with particular reference to enterovirulent Escherichia coli strains. Int J Poult Sci. 2013;12:430–435. doi: 10.3923/ijps.2013.430.435. - DOI
-
- Messens W, Grijspeerdt K, Herman L. Eggshell penetration by Salmonella : a review. Worlds Poult Sci J. 2005;61(March):71–86. doi: 10.1079/WPS200443. - DOI
-
- Adesiyun A, Offiah N, Seepersadsingh N, Rodrigo S, Lashley V, Musai L. Antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella spp. and Escherichia coli isolated from table eggs. Food Control. 2007;18:306–311. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2005.10.013. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

