Peroral endoscopic myotomy: a literature review and the first UK case series
- PMID: 28148574
- PMCID: PMC6297590
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmedicine.17-1-22
Peroral endoscopic myotomy: a literature review and the first UK case series
Abstract
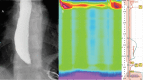
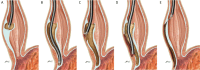
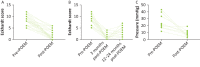
Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) is an established treatment for primary achalasia. It has gained endorsement from the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy with increasing clinical acceptance since the first procedure, performed in Japan in 2008. The first successful POEM in the UK was performed in November 2013 at King's College Hospital and this article presents the first UK case series. Prospective data were collected at 3 and 12-24 months for consecutive patients undergoing POEM. Post-POEM gastro-oesophageal reflux health-related quality of life scale (GORD-HRQoL) score was recorded. Statistical comparisons were made using paired non-parametric testing. In an initial series of 33 consecutive prospectively followed patients (12 female; 49.5±13 years; median follow-up 9 (3-28) months; 58% having had previous intervention), a 91% success rate has been achieved at 3 months. To date, 16 patients have reached the 12-month time point, with 13 (81%) sustaining response. This case series compares well with international cohorts and demonstrates excellent long-term safety and favourable efficacy.
Keywords: Achalasia; endoscopy; manometry; oesophageal motility disorders.
© Royal College of Physicians 2017. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Peroral endoscopic myotomy: anterior versus posterior approach: a randomized single-blinded clinical trial.Gastrointest Endosc. 2020 Feb;91(2):288-297.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2019.07.034. Epub 2019 Aug 10. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020. PMID: 31408652 Clinical Trial.
-
Peroral endoscopic shorter versus longer myotomy for the treatment of achalasia: a comparative retrospective study.Esophagus. 2020 Oct;17(4):477-483. doi: 10.1007/s10388-020-00739-4. Epub 2020 May 2. Esophagus. 2020. PMID: 32361976
-
Peroral endoscopic myotomy for esophageal achalasia: outcomes of the first over 100 patients with short-term follow-up.Surg Endosc. 2016 Nov;30(11):4817-4826. doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-4813-1. Epub 2016 Mar 1. Surg Endosc. 2016. PMID: 26932548
-
Updated Systematic Review of Achalasia, with a Focus on POEM Therapy.Dig Dis Sci. 2020 Jan;65(1):38-65. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05784-3. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Dig Dis Sci. 2020. PMID: 31451984
-
Peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014 Jan;26(1):3-12. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12257. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014. PMID: 24304406 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Outcomes and Complications for Achalasia Patients Admitted After Per-Oral Endoscopic Myotomy.Gastroenterology Res. 2023 Jun;16(3):141-148. doi: 10.14740/gr1617. Epub 2023 Jun 11. Gastroenterology Res. 2023. PMID: 37351078 Free PMC article.
-
Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) vs pneumatic dilation (PD) in treatment of achalasia: A meta-analysis of studies with ≥ 12-month follow-up.Endosc Int Open. 2021 Jul;9(7):E1097-E1107. doi: 10.1055/a-1483-9406. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Endosc Int Open. 2021. PMID: 34222636 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

