Calcium signals drive cell shape changes during zebrafish midbrain-hindbrain boundary formation
- PMID: 28148652
- PMCID: PMC5385936
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E16-08-0561
Calcium signals drive cell shape changes during zebrafish midbrain-hindbrain boundary formation
Abstract
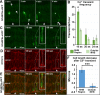
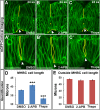
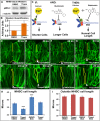
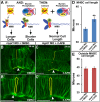
One of the first morphogenetic events in the vertebrate brain is the formation of the highly conserved midbrain-hindbrain boundary (MHB). Specific cell shape changes occur at the point of deepest constriction of the MHB, the midbrain-hindbrain boundary constriction (MHBC), and are critical for proper MHB formation. These cell shape changes are controlled by nonmuscle myosin II (NMII) motor proteins, which are tightly regulated via the phosphorylation of their associated myosin regulatory light chains (MRLCs). However, the upstream signaling pathways that initiate the regulation of NMII to mediate cell shape changes during MHB morphogenesis are not known. We show that intracellular calcium signals are critical for the regulation of cell shortening during initial MHB formation. We demonstrate that the MHB region is poised to respond to calcium transients that occur in the MHB at the onset of MHB morphogenesis and that calcium mediates phosphorylation of MRLC specifically in MHB tissue. Our results indicate that calmodulin 1a (calm1a), expressed specifically in the MHB, and myosin light chain kinase together mediate MHBC cell length. Our data suggest that modulation of NMII activity by calcium is critical for proper regulation of cell length to determine embryonic brain shape during development.
© 2017 Sahu, Visetsouk, et al. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). Two months after publication it is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
Figures
References
-
- Ashworth R, Devogelaere B, Fabes J, Tunwell RE, Koh KR, De Smedt H, Patel S. Molecular and functional characterization of inositol trisphosphate receptors during early zebrafish development. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:13984–13993. - PubMed
-
- Barreda EG, Avila J. Tau regulates the subcellular localization of calmodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;408:500–504. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev. 2000;1:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Bootman MD, Collins TJ, Mackenzie L, Roderick HL, Berridge MJ, Peppiatt CM. 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) is a reliable blocker of store-operated Ca2+ entry but an inconsistent inhibitor of InsP3-induced Ca2+ release. FASEB J. 2002;16:1145–1150. - PubMed
-
- Bramlage P, Joss G, Staudt A, Jarrin A, Podlowski S, Baumann G, Stangl K, Felix SB, Stangl V. Computer-aided measurement of cell shortening and calcium transients in adult cardiac myocytes. Biotechnol Prog. 2001;17:929–934. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

