Endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibition attenuates hypertensive chronic kidney disease through reduction in proteinuria
- PMID: 28148966
- PMCID: PMC5288651
- DOI: 10.1038/srep41572
Endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibition attenuates hypertensive chronic kidney disease through reduction in proteinuria
Abstract
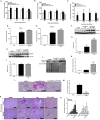
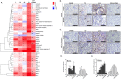
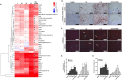
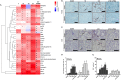
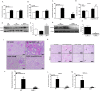
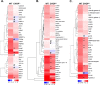
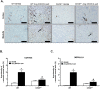
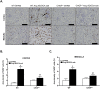
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is implicated in chronic kidney disease (CKD) development in patients and in animal models. Here we show that ER stress inhibition through 4-phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA) administration decreases blood pressure, albuminuria, and tubular casts in an angiotensin II/deoxycorticosterone acetate/salt murine model of CKD. Lower albuminuria in 4-PBA-treated mice was associated with higher levels of cubilin protein in renal tissue membrane fractions. 4-PBA decreased renal interstitial fibrosis, renal CD3+ T-cell and macrophage infiltration, mRNA expression of TGFβ1, Wnt signaling molecules, and ER stress-induced pro-inflammatory genes. CHOP deficient mice that underwent this model of CKD developed hypertension comparable to wild type mice, but had less albuminuria and tubular casts. CHOP deficiency resulted in higher nephrin levels and decreased glomerulosclerosis compared to wild type mice; this effect was accompanied by lower macrophage infiltration and fibrosis. Our findings portray ER stress inhibition as a means to alleviate hypertensive CKD by preserving glomerular barrier integrity and tubular function. These results demonstrate ER stress modulation as a novel target for preserving renal function in hypertensive CKD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibition limits the progression of chronic kidney disease in the Dahl salt-sensitive rat.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Jan 1;312(1):F230-F244. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00119.2016. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28069662
-
TDAG51 induces renal interstitial fibrosis through modulation of TGF-β receptor 1 in chronic kidney disease.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 8;12(10):921. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04197-3. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34625532 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of RTN1A attenuates ER stress and kidney injury in albumin overload-induced nephropathy.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Mar 1;310(5):F409-15. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00485.2015. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26739891 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, a Driver or an Innocent Bystander in Endothelial Dysfunction Associated with Hypertension?Curr Hypertens Rep. 2017 Aug;19(8):64. doi: 10.1007/s11906-017-0762-x. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2017. PMID: 28717886 Review.
-
Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis and Evolution of Chronic Kidney Disease: Untangling Ariadne's Thread.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 29;20(15):3711. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153711. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31362427 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reduction of stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD) contributes muscle atrophy through the excess endoplasmic reticulum stress in chronic kidney disease.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2020 Sep;67(2):179-187. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.20-24. Epub 2020 Jun 9. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2020. PMID: 33041516 Free PMC article.
-
Nifedipine Upregulates ATF6-α, Caspases -12, -3, and -7 Implicating Lipotoxicity-Associated Renal ER Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 29;21(9):3147. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093147. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32365658 Free PMC article.
-
4-Phenylbutyric Acid Treatment Reduces Low-Molecular-Weight Proteinuria in a Clcn5 Knock-in Mouse Model for Dent Disease-1.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 25;25(15):8110. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158110. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125679 Free PMC article.
-
4-Phenylbutyric acid, a potent endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibitor, attenuates the severity of collagen-induced arthritis in mice via inhibition of proliferation and inflammatory responses of synovial fibroblasts.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2021 Jul;37(7):604-615. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12376. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33759334 Free PMC article.
-
Kaempferol mitigates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Induced Cell Death by targeting caspase 3/7.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 1;8(1):2189. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20499-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29391535 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jha V. et al.. Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 382, 260–272 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Dickhout J. G. & Krepinsky J. C. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and renal disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 11, 2341–2352 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Inagi R., Ishimoto Y. & Nangaku M. Proteostasis in endoplasmic reticulum--new mechanisms in kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 10, 369–378 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Dickhout J. G., Carlisle R. E. & Austin R. C. Interrelationship between cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease: endoplasmic reticulum stress as a mediator of pathogenesis. Circ Res 108, 629–642 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

