Can We Perform Distal Nerve Block Instead of Brachial Plexus Nerve Block Under Ultrasound Guidance for Hand Surgery?
- PMID: 28149139
- PMCID: PMC5268596
- DOI: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2016.0256
Can We Perform Distal Nerve Block Instead of Brachial Plexus Nerve Block Under Ultrasound Guidance for Hand Surgery?
Abstract
Objective: Distal nerve blocks are used in the event of unsuccessful blocks as rescue techniques. The primary purpose of this study was to determine the sufficiency for anesthesia of distal nerve block without the need for deep sedation or general anesthesia. The secondary purpose was to compare block performance times, block onset times, and patient and surgeon satisfaction.
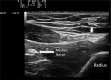
Materials and methods: Patients who underwent hand surgery associated with the innervation area of the radial and median nerves were included in the study. Thirty-four patients who were 18-65 years old and American Society of Anesthesiologists grade I-III and who were scheduled for elective hand surgery under conscious nerve block anesthesia were randomly included in an infraclavicular block group (Group I, n=17) or a radial plus median block group (Group RM, n=17). The block performance time, block onset time, satisfaction of the patient and surgeon, and number of fentanyl administrations were recorded.
Results: The numbers of patients who needed fentanyl administration and conversion to general anesthesia were the same in Group I and Group RM and there was no statistically significant difference (p>0.05). The demographics, surgery times, tourniquet times, block perfomance times, and patient and surgeon satisfaction of the groups were similar and there were no statistically significant differences (p>0.05). There was a statistically significant difference in block onset times between the groups (p<0.05).
Conclusions: Conscious hand surgery can be performed under distal nerve block anesthesia safely and successfully.
Amaç: Distal sinir blokları başarısız proksimal blok uygulamalarında tamamlayıcı blok olarak kullanılmaktadır. Bu çalışmanın primer amacı genel anestezi ve derin sedasyona ihtiyaç olmadan distal sinir bloklarının yeterli anestezi sağlayıp sağlamadığını değerlendirmektir. İkinci amacı ise blok uygulama ve blok gelişme zamanları, hasta ve cerrah memnuniyetlerini karşılaştırmaktır.
Gereç ve yöntem: 18–65 yaş, ASA I-III, Radial ve median sinir innervasyon alanlarını içeren elektif el cerrahisi geçirecek 34 hasta çalışmaya alındı ve hastalar randomize olarak infraklavikular blok grubu (Grup I, n=17) ve radial + median blok grubuna (Grup RM, n=17) dahil edildi. Blok uygulama ve blok gelişme zamanları ile hasta ve cerrah memnuniyetleri kayıt altına alındı.
Bulgular: Genel anesteziye dönüş ve fentanil ihtiyacı olan hasta sayısı her iki grupta da aynıydı ve istatistiksel bir fark tespit edilmedi (p>0,05). Demografik veriler, ortalama cerrahi zamanı, turnike zamanı, blok uygulama zamanı, hasta ve cerrah memnuniyeti açısında gruplar arasında anlamlı bir istatistiksel fark yoktu (p>0,05). Blok gelişme zamanlarında ise gruplar arasında istatistiksel olarak anlamlı bir farklılık tespit edildi (p<0,05).
Sonuç: Uyanık el cerrahisi distal sinir blokları ile güvenli ve başarılı bir şekilde uygulanabilir.
Keywords: Distal nerve block; brachial plexus; median nerve; proximal nerve block; radial nerve.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distal Peripheral Nerve Blocks in the Forearm as an Alternative to Proximal Brachial Plexus Blockade in Patients Undergoing Hand Surgery: A Prospective and Randomized Pilot Study.J Hand Surg Am. 2016 Oct;41(10):969-977. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2016.07.092. Epub 2016 Aug 11. J Hand Surg Am. 2016. PMID: 27524691 Clinical Trial.
-
A Comparison of Distal Nerve Blocks and Brachial Plexus Blocks in Terms of Block Success, Block-related Characteristics, Time to Discharge and Patient Satisfaction.J Hand Surg Asian Pac Vol. 2023 Aug;28(4):446-452. doi: 10.1142/S2424835523500509. Epub 2023 Sep 25. J Hand Surg Asian Pac Vol. 2023. PMID: 37758499
-
Effectiveness of ondansetron as an adjunct to lidocaine intravenous regional anesthesia on tourniquet pain and postoperative pain in patients undergoing elective hand surgery: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):27-38. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1768. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447005
-
Ultrasound guided distal peripheral nerve block of the upper limb: A technical review.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Jul-Sep;31(3):296-307. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.161654. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26330706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brachial plexus blocks: a review of approaches and techniques.Can J Anaesth. 2007 Aug;54(8):662-74. doi: 10.1007/BF03022962. Can J Anaesth. 2007. PMID: 17666721 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of ultrasound-guided forearm nerve block versus forearm intravenous regional anaesthesia in patients undergoing carpal tunnel release: A randomized controlled trial.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 19;16(2):e0246863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246863. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33606754 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ultrasound-guided Mid-humeral Radial Nerve Block Provides Sufficient Surgical Anesthesia at Hand Dorsum: A Novel Method and Report of Three Cases.Cureus. 2019 Jan 24;11(1):e3949. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3949. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 30937247 Free PMC article.
-
Erector Spinae Plane Block Catheter Insertion under Ultrasound Guidance for Thoracic Surgery: Case Series of Three Patients.Eurasian J Med. 2018 Oct;50(3):204-206. doi: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2018.18147. Eurasian J Med. 2018. PMID: 30515044 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized controlled trial evaluating the hemodynamic impact of ultrasound-guided great auricular nerve block in middle ear microsurgery.BMC Anesthesiol. 2020 Sep 15;20(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s12871-020-01155-y. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020. PMID: 32933470 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Lam NC, Charles M, Mercer D, et al. A triple-masked, randomized controlled trial comparing ultrasound-guided brachial plexus and distal peripheral nerve block anesthesia for outpatient hand surgery. Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2014;324083:7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/324083. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marhofer P, Frickey N. Ultrasonographic guidance in pediatric regional anesthesia Part 1: Theoretical background. Paediatr Anaesth. 2006;16:1008–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9592.2006.02020.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anagnostopoulou S, Saranteas T, Chantzi C, Dimitriou V, Karabinis A, Kostopanagiotou G. Ultrasound identification of the radial nerve and its divisions. Is rescue nerve block at or below the elbow possible? Anaesth Intensive Care. 2008;36:457–9. - PubMed
-
- Gray AT, Schafhalter-Zoppoth I. Ultrasound guidance for ulnar nerve block in the forearm. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2003;28:335–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/00115550-200303000-00014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Soberón JR, Bhatt NR, Nossaman BD, Duncan SF, Patterson ME, Sisco-Wise LE. Distal peripheral nerve blockade for patients undergoing hand surgery: a pilot study. Hand (N Y) 2015;10:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11552-014-9680-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical