Identification of Submergence-Responsive MicroRNAs and Their Targets Reveals Complex MiRNA-Mediated Regulatory Networks in Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn)
- PMID: 28149304
- PMCID: PMC5241310
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00006
Identification of Submergence-Responsive MicroRNAs and Their Targets Reveals Complex MiRNA-Mediated Regulatory Networks in Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn)
Abstract
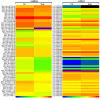
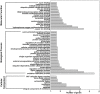
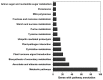
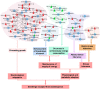
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous non-coding RNAs with important regulatory functions in plant development and stress responses. However, their population abundance in lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn) has so far been poorly described, particularly in response to stresses. In this work, submergence-related miRNAs and their target genes were systematically identified, compared, and validated at the transcriptome-wide level using high-throughput sequencing data of small RNA, Mrna, and the degradome. A total of 128 known and 20 novel miRNAs were differentially expressed upon submergence. We identified 629 target transcripts for these submergence-responsive miRNAs. Based on the miRNA expression profiles and GO and KEGG annotation of miRNA target genes, we suggest possible molecular responses and physiological changes of lotus in response to submergence. Several metabolic, physiological and morphological adaptations-related miRNAs, i.e., NNU_far-miR159, NNU_gma-miR393h, and NNU_aly-miR319c-3p, were found to play important regulatory roles in lotus response to submergence. This work will contribute to a better understanding of miRNA-regulated adaption responses of lotus to submergence stress.
Keywords: Nelumbo nucifera; high-throughput sequencing; microRNAs; small RNA; submergence.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Small RNA and degradome profiling reveals miRNA regulation in the seed germination of ancient eudicot Nelumbo nucifera.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 26;17(1):684. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3032-4. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27565736 Free PMC article.
-
Time-course analysis and transcriptomic identification of key response strategies to complete submergence in Nelumbo nucifera.Hortic Res. 2022 Feb 11;9:uhac001. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhac001. Online ahead of print. Hortic Res. 2022. PMID: 35147174 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of miRNAs expression reveals novel insights into adventitious root formation in lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.).Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Jun;46(3):2893-2905. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-04749-z. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30864113
-
Small RNA and Transcriptome Sequencing Reveals miRNA Regulation of Floral Thermogenesis in Nelumbo nucifera.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 8;21(9):3324. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093324. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32397143 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances on bioactive compounds, biosynthesis mechanism, and physiological functions of Nelumbo nucifera.Food Chem. 2023 Jun 30;412:135581. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.135581. Epub 2023 Jan 27. Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 36731239 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of RNAi technology: a novel approach to navigate abiotic stresses.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Nov;49(11):10975-10993. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07871-7. Epub 2022 Sep 4. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36057876 Review.
-
Small RNA sequencing identifies cucumber miRNA roles in waterlogging-triggered adventitious root primordia formation.Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Dec;46(6):6381-6389. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-05084-z. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31538299
-
Involvement of miR775 in the Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase in Maize (Zea mays L.) Leaves Under Hypoxia.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 21;26(3):865. doi: 10.3390/ijms26030865. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940636 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Expression of Maize and Teosinte microRNAs under Submergence, Drought, and Alternated Stress.Plants (Basel). 2020 Oct 15;9(10):1367. doi: 10.3390/plants9101367. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33076374 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially Expressed microRNAs and Target Genes Associated with Plastic Internode Elongation in Alternanthera philoxeroides in Contrasting Hydrological Habitats.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Dec 5;8:2078. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.02078. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 29259617 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asha S., Nisha J., Soniya E. (2013). In silico characterisation and phylogenetic analysis of two evolutionarily conserved miRNAs (miR166 and miR171) from Black Pepper (Piper nigrum L.). Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 31, 707–718. 10.1007/s11105-012-0532-5 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

