Splint-assisted disc plication surgery
- PMID: 28149454
- PMCID: PMC5231793
- DOI: 10.11138/ads/2016.7.3.078
Splint-assisted disc plication surgery
Abstract
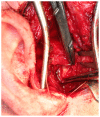
Chronic disc displacement may lead to long-term pain. Temporomandibular joint surgery is reserved for those patients whose symptoms remain severe despite conservative treatment. We looked at the of effect of modified meniscopexy on patients with chronic disc displacement without reduction who did not respond to non-surgical pain management treatment. In this retrospective study a total of 59 joints was treated and all patients except one underwent splint assisted bilateral meniscopexy: this patient had splint assisted unilateral meniscopexy. At the time of presentation and following treatment all patients underwent clinical examination and were required to complete a pain and functional questionnaire. All patients reported improvement following treatment.
Keywords: meniscopexy; splint; temporomandibular joint.
Figures
References
-
- Leresche L. Epidemiology of temporomandibular disorders: implications for the investigation of etiologic factors. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1997;8:291–305. - PubMed
-
- Attanasio G, Leonardi A, Arangio P, Minni A, Covelli E, Pucci R, Russo FY, De Seta E, Di Paolo C, Cascone P. Tinnitus in patients with temporo-mandibular joint disorder: Proposal for a new treatment protocol. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015;43(5):724–7. - PubMed
-
- Manfredini D, Guarda-Nardini N, Winocur E, Piccotti F, Ahlberg J, Lobbezoo F. Research diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders: a systematic review of axis I epidemiologic findings. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011;112:453–462. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka E, Detamore MS, Mercuri LG. Degenerative disorders of the temporomandibular joint: etiology, diagnosis and treatment. J Dent Res. 2008;87:296–307. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources