Tracheobronchial tuberculosis
- PMID: 28149582
- PMCID: PMC5227251
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2016.12.75
Tracheobronchial tuberculosis
Abstract
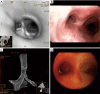
Tracheobronchial tuberculosis (TBTB) is reported in approximately 10% to 39% of the patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. It is defined as the tubercle infection of the trachea and or bronchi. Due to its non-specific presentation, insidious onset and normal chest radiography in about 10-20% of the patients, the diagnosis is delayed. Bronchoscopy is the most definite method of diagnosis which provides adequate specimens for microbiological and histopathological diagnosis. Tracheobronchial stenosis is one of the most common long term complications of TBTB resulting in significant morbidity. It is estimated that 90% of patients with TBTB have some degree of tracheal and or bronchial stenosis. In this review article, we will discuss the pathogenesis, symptoms, imaging, bronchoscopic findings, and treatment of TBTB and management of tracheobronchial stenosis.
Keywords: Tuberculosis induced stenosis; bronchial stenosis; endobronchial stenosis; endobronchial tuberculosis; tracheobronchial stenosis; tracheobronchial tuberculosis (TBTB).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Um SW, Yoon YS, Lee SM, et al. Predictors of persistent airway stenosis in patients with endobronchial tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2008;12:57-62. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
