Hepatitis C virus and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: A minireview
- PMID: 28149648
- PMCID: PMC5272953
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2016.11.005
Hepatitis C virus and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: A minireview
Abstract
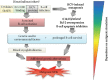
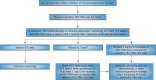
B-cell NHL is strongly associated with HCV that was proved in the last 2 decades. The most common HCV infection related B-NHL subtypes include MZL and DLBCL lymphomas. HCV-positive NHL patients usually present with older age at diagnosis, higher LDH, and more extranodal disease. The standard chemo-immunotherapy tolerance is generally good. Antiviral treatment achieves virological and hematological remission in HCV associated indolent lymphoma. More aggressive lymphoma requires combination of antiviral treatment and chemotherapy. New generation of HCV antiviral drugs is safe and is highly efficacious. Regimens including DAAs appear promising options as they can reduce the HCV-associated NHL incidence by dramatically lowering the HCV chronic carriers.
Keywords: Antiviral treatment; Hepatitis C virus; Non-Hodgkin lymphoma; Pathogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Durand T., Di Liberto G., Colman H., Cammas A., Boni S., Marcellin P. Occult infection of peripheral B cells by hepatitis C variants which have low translational efficiency in cultured hepatocytes. Gut. 2010;59:934–942. - PubMed
-
- Simonetti R.G., Camma C., Fiorello F., Cottone M., Rapicetta M., Marino L. Hepatitis C virus infection as a risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. A case-control study. Ann Intern Med. 1992;116:97–102. - PubMed
-
- Waked I., Doss W., El-Sayed M.H., Estes C., Razavi H., Shiha G. The current and future disease burden of chronic hepatitis C virus infection in Egypt. Arab J Gastroenterol. 2014;15:45–52. - PubMed
-
- Shepard C.W., Finelli L., Alter M.J. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5:558–567. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources