Hepatic caveolin-1 is enhanced in Cyp27a1/ApoE double knockout mice
- PMID: 28149711
- PMCID: PMC5275772
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.12123
Hepatic caveolin-1 is enhanced in Cyp27a1/ApoE double knockout mice
Abstract
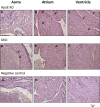
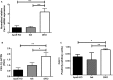
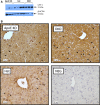
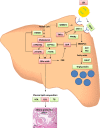
Sterol 27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1) is involved in bile acid synthesis and cholesterol homoeostasis. Cyp27a1(-/-)/Apolipoprotein E(-/-) double knockout mice (DKO) fed a western diet failed to develop atherosclerosis. Caveolin-1 (CAV-1), the main component of caveolae, is associated with lipid homoeostasis and has regulatory roles in vascular diseases. We hypothesized that liver CAV-1 would contribute to the athero-protective mechanism in DKO mice. Cyp27a1(+/+)/ApoE(-/-) (ApoE KO), Cyp27a1(+/-)/ApoE(-/-) (het), and DKO mice were fed a western diet for 2 months. Atherosclerotic plaque and CAV-1 protein were quantified in aortas. Hepatic Cav-1 mRNA was assessed using qPCR, CAV-1 protein by immunohistochemistry and western blotting. Total hepatic and plasma cholesterol was measured using chemiluminescence. Cholesterol efflux was performed in RAW264.7 cells, using mice plasma as acceptor. CAV-1 protein expression in aortas was increased in endothelial cells of DKO mice and negatively correlated with plaque surface (P < 0.05). In the liver, both CAV-1 protein and mRNA expression doubled in DKO, compared to ApoE KO and het mice (P < 0.001 for both) and was negatively correlated with total hepatic cholesterol (P < 0.05). Plasma from DKO, ApoE KO and het mice had the same efflux capacity. In the absence of CYP27A1, CAV-1 overexpression might have an additional athero-protective role by partly overcoming the defect in CYP27A1-mediated cholesterol efflux.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; cholesterol efflux; cholesterol metabolism; liver.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Downregulation of Cyp7a1 by Cholic Acid and Chenodeoxycholic Acid in Cyp27a1/ApoE Double Knockout Mice: Differential Cardiovascular Outcome.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Oct 28;11:586980. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.586980. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33193099 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Cyp27A1 gene dosage on atherosclerosis development in ApoE-knockout mice.FASEB J. 2014 Mar;28(3):1198-209. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-233791. Epub 2013 Dec 10. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24327605 Free PMC article.
-
Sterol 27-hydroxylase gene dosage and the antiatherosclerotic effect of Rifampicin in mice.Biosci Rep. 2018 Jan 25;38(1):BSR20171162. doi: 10.1042/BSR20171162. Print 2018 Feb 28. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29191818 Free PMC article.
-
PPARgamma1-induced caveolin-1 enhances cholesterol efflux and attenuates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice.J Vasc Res. 2010;47(1):69-79. doi: 10.1159/000235927. Epub 2009 Sep 3. J Vasc Res. 2010. PMID: 19729954
-
TSLPR deficiency attenuates atherosclerotic lesion development associated with the inhibition of TH17 cells and the promotion of regulator T cells in ApoE-deficient mice.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Nov;76:33-45. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.07.003. Epub 2014 Aug 10. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25117469
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial Cholesterol Metabolites in a Bile Acid Synthetic Pathway Drive Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Revised "Two-Hit" Hypothesis.Cells. 2023 May 20;12(10):1434. doi: 10.3390/cells12101434. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37408268 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Escher G, Hoang A, Georges S, Tchoua U, El‐Osta A, Krozowski Z and Sviridov D (2005) Demethylation using the epigenetic modifier, 5‐azacytidine, increases the efficiency of transient transfection of macrophages. J Lipid Res 46, 356–365. - PubMed
-
- Escher G, Krozowski Z, Croft KD and Sviridov D (2003) Expression of sterol 27‐hydroxylase (CYP27A1) enhances cholesterol efflux. J Biol Chem 278, 11015–11019. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

