Tissue sodium accumulation and peripheral insulin sensitivity in maintenance hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 28150400
- PMCID: PMC5476848
- DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12179
Tissue sodium accumulation and peripheral insulin sensitivity in maintenance hemodialysis patients
Abstract
Background: Recent data suggest that sodium (Na+ ) is stored in the muscle and skin without commensurate water retention in maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) patients. In this study, we hypothesized that excessive Na+ accumulation would be associated with abnormalities in peripheral insulin action.
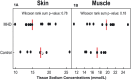
Methods: Eleven MHD patients and eight controls underwent hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic-euaminoacidemic clamp studies to measure glucose (GDR) and leucine disposal rates (LDR), as well as lower left leg 23 Na magnetic resonance imaging to measure Na+ concentration in the muscle and skin tissue.
Results: The median GDR and LDR levels were lower, and the median muscle Na+ concentration was higher in MHD patients compared with controls. No significant difference was found regarding skin Na+ concentration between group comparisons. Linear regression revealed inverse relationships between muscle Na+ concentration and GDR and LDR in MHD patients, whereas no relationship was observed in controls. There was no association between skin Na+ content and GDR or LDR in either MHD patients or controls.
Conclusions: These data suggest that excessive muscle Na+ content might be a determinant of IR in MHD patients, although the causality and mechanisms remain to be proven.
Keywords: Glucose disposal rate; Insulin resistance; Leucine disposal rate; Muscle sodium content.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the Society on Sarcopenia, Cachexia and Wasting Disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Carrero JJ, Stenvinkel P, Cuppari L, Ikizler TA, Kalantar‐Zadeh K, Kaysen G, Mitch WE, Price SR, Wanner C, Wang AY, et al Etiology of the protein‐energy wasting syndrome in chronic kidney disease: a consensus statement from the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism (ISRNM). J Ren Nutr 2013;23:77–90. - PubMed
-
- Mak RH. Insulin and its role in chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 2008;23:355–362. - PubMed
-
- Siew ED, Pupim LB, Majchrzak KM, Shintani A, Flakoll PJ, Ikizler TA. Insulin resistance is associated with skeletal muscle protein breakdown in non‐diabetic chronic hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 2007;71:146–152. - PubMed
-
- Siew ED, Ikizler TA. Insulin resistance and protein energy metabolism in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease. Semin Dial 2010;23:378–382. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

