Temporal course of implicit emotion regulation during a Priming-Identify task: an ERP study
- PMID: 28150801
- PMCID: PMC5288784
- DOI: 10.1038/srep41941
Temporal course of implicit emotion regulation during a Priming-Identify task: an ERP study
Abstract
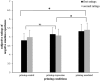
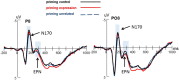
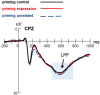
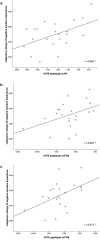
Implicit emotion regulation defined as goal-driven processes modulates emotion experiences and responses automatically without awareness. However, the temporal course of implicit emotion regulation is not clear. To address these issues, we adopted a new Priming-identify task (PI task) to manipulate implicit emotion regulation directly and observed the changes of early (N170), middle (early posterior negativity, EPN), and late event-related potentials (ERPs) components (late positivity potentials, LPP) under the different implicit emotion regulation conditions. The behavioral results indicated that the PI task manipulated subjective emotion experience effectively by priming emotion regulation goals. The ERP results found that implicit emotion regulation induced more negative N170 without altering the EPN and the LPP amplitudes, indicating that implicit emotion regulation occured automatically in the early perceptual stage not in the late selective attention stage of emotion processing. The correlation analysis also found the enlarged N170 was associated with decreased negative emotion subjective rating, suggesting that the N170 was probably an effective index of implicit emotion regulation. These observations imply that implicit emotion regulation probabbly occurs in the early stage of emotion processing automatically without consciousness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Implicit Emotion Regulation Deficits in Trait Anxiety: An ERP Study.Front Hum Neurosci. 2018 Sep 28;12:382. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2018.00382. eCollection 2018. Front Hum Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30323748 Free PMC article.
-
Implicit emotion regulation deficits in individuals with high schizotypal traits: an ERP study.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 3;10(1):3882. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60787-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32127580 Free PMC article.
-
Implicit emotion regulation affects outcome evaluation.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2015 Jun;10(6):824-31. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsu124. Epub 2014 Oct 20. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25332404 Free PMC article.
-
Event-related potentials, emotion, and emotion regulation: an integrative review.Dev Neuropsychol. 2010;35(2):129-55. doi: 10.1080/87565640903526504. Dev Neuropsychol. 2010. PMID: 20390599 Review.
-
Implicit and explicit categorization of natural scenes.Prog Brain Res. 2006;156:53-65. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)56003-0. Prog Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 17015074 Review.
Cited by
-
The Emotion-Regulation Benefits of Implicit Reappraisal in Clinical Depression: Behavioral and Electrophysiological Evidence.Neurosci Bull. 2023 Jun;39(6):973-983. doi: 10.1007/s12264-022-00973-z. Epub 2022 Nov 10. Neurosci Bull. 2023. PMID: 36355339 Free PMC article.
-
Offline rTMS inhibition of the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex impairs reappraisal efficacy.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 10;12(1):21394. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24629-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36496506 Free PMC article.
-
Processing of emotional connotations in Chinese monomorphic and compound words reflected by the early posterior negativity.Front Psychol. 2024 Aug 9;15:1426383. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1426383. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39184939 Free PMC article.
-
High Gamma Band EEG Closely Related to Emotion: Evidence From Functional Network.Front Hum Neurosci. 2020 Mar 24;14:89. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.00089. eCollection 2020. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32265674 Free PMC article.
-
Implicit emotion regulation improves arithmetic performance: An ERP study.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2022 Jun;22(3):574-585. doi: 10.3758/s13415-021-00979-6. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35091988
References
-
- Gross J. J. & Thompson R. A. In Handbook of emotion regulation (ed Gross J. J.) (Guilford Press., New York, 2007).
-
- Mauss I. B., Cook C. L. & Gross J. J. Automatic Emotion Regulation during Anger Provocation. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology 43, 698–711, doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2006.07.003 (2007). - DOI
-
- Bargh J. A. & Williams L. E. In Handbook of Emotion Regulation (ed Gross J. J.) (Guilford Press, New York, 2007).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

