Zika virus protection by a single low-dose nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccination
- PMID: 28151488
- PMCID: PMC5344708
- DOI: 10.1038/nature21428
Zika virus protection by a single low-dose nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccination
Abstract
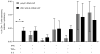
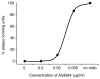
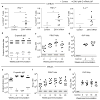
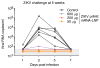
Zika virus (ZIKV) has recently emerged as a pandemic associated with severe neuropathology in newborns and adults. There are no ZIKV-specific treatments or preventatives. Therefore, the development of a safe and effective vaccine is a high priority. Messenger RNA (mRNA) has emerged as a versatile and highly effective platform to deliver vaccine antigens and therapeutic proteins. Here we demonstrate that a single low-dose intradermal immunization with lipid-nanoparticle-encapsulated nucleoside-modified mRNA (mRNA-LNP) encoding the pre-membrane and envelope glycoproteins of a strain from the ZIKV outbreak in 2013 elicited potent and durable neutralizing antibody responses in mice and non-human primates. Immunization with 30 μg of nucleoside-modified ZIKV mRNA-LNP protected mice against ZIKV challenges at 2 weeks or 5 months after vaccination, and a single dose of 50 μg was sufficient to protect non-human primates against a challenge at 5 weeks after vaccination. These data demonstrate that nucleoside-modified mRNA-LNP elicits rapid and durable protective immunity and therefore represents a new and promising vaccine candidate for the global fight against ZIKV.
Figures

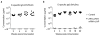
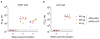
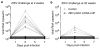
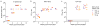
Comment in
-
Zika Virus Vaccines - A Full Field and Looking for the Closers.N Engl J Med. 2017 May 11;376(19):1883-1886. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcibr1701402. N Engl J Med. 2017. PMID: 28490001 No abstract available.
References
-
- Weissman D. mRNA transcript therapy. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015;14:265–281. - PubMed
-
- Sahin U, Kariko K, Tureci O. mRNA-based therapeutics--developing a new class of drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13:759–780. - PubMed
-
- Dick GW, Kitchen SF, Haddow AJ. Zika virus. I. Isolations and serological specificity. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1952;46:509–520. - PubMed

