Pediatric Hodgkin Lymphoma: Predictive value of interim 18F-FDG PET/CT in therapy response assessment
- PMID: 28151888
- PMCID: PMC5293451
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005973
Pediatric Hodgkin Lymphoma: Predictive value of interim 18F-FDG PET/CT in therapy response assessment
Abstract
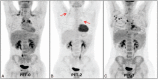
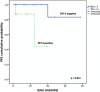
We investigated the prognostic value of interim F-FDG PET/CT (PET-2) in pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma (pHL), evaluating both visual and semiquantitative analysis.Thirty pHL patients (age ≤16) underwent serial F-FDG PET/CT: at baseline (PET-0), after 2 cycles of chemotherapy (PET-2) and at the end of first-line chemotherapy (PET-T). PET response assessment was carried out visually according to the Deauville Score (DS), as well as semiquantitatively by using the semiquantitative parameters reduction from PET-0 to PET-2 (ΔΣSUVmax0-2, ΔΣSUVmean0-2). Final clinical response assessment (outcome) at the end of first-line chemotherapy was the criterion standard, considering patients as responders (R) or nonresponders (NR). Disease status was followed identifying patients with absence or relapsed/progression disease (mean follow-up: 24 months, range 3-78).Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy of visual and semiquantitative assessment were calculated; furthermore, Fisher exact test was performed to evaluate the association between both visual and semiquantitative assessment and outcome at the end of the first-line chemotherapy. The prognostic capability of PET-2 semiquantitative parameters was calculated by ROC analysis and expressed as area under curve (AUC). Finally, progression-free survival (PFS) was analyzed according to PET-2 results based on the 5-point scale and semiquantitative criteria, using the Kaplan-Meier method.Based on the outcome at the end of first-line chemotherapy, 5 of 30 patients were NR, the remnant 25 of 30 were R. Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and accuracy of visual analysis were 60%,72%,30%,90%,70%; conversely, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and accuracy of semiquantitative assessment were 80%, 92%, 66.7%, 95.8%, 90%. The highest AUC resulted for ΔΣSUVmax0-2 (0.836; cut-off <12.5; sensitivity 80%; specificity 91%). The association between ΔΣSUVmax0-2 and outcome at the end of first-line chemotherapy resulted to have a strong statistical significance (P = 0.0026). Both methods demonstrated to influence PFS, even if the semiquantitative assessment allowed a more accurate identification of patients with a high risk of treatment failure (P = 0.005).Our preliminary results showed that PET-2 visual assessment, by using Deauville criteria, can be improved by using the semiquantitative analysis. The SUV max reduction (ΔΣSUVmax0-2) evaluation might provide a support for the interpretation of intermediate scores, predicting with good confidence those patients who will have a poor outcome and require alternative therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Qiu L, Chen Y, Wu J. The role of 18F-FDG PET and 18F-FDG PET/CT in the evaluation of pediatric Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Hell J Nucl Med 2013;16:230–6. - PubMed
-
- Sharma P, Gupta A, Patel C, et al. Pediatric lymphoma: metabolic tumor burden as a quantitative index for treatment response evaluation. Ann Nucl Med 2012;26:58–66. - PubMed
-
- Furth C, Steffen IG, Amthauer H, et al. Early and late therapy response assessment with [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in pediatric Hodgkin's lymphoma: analysis of a prospective multicenter trial. J Clin Oncol 2009;27:4385–91. - PubMed
-
- Aleman BM, van den Belt-Dusebout AW, Klokman WJ, et al. Long-term cause specific mortality of patients treated for Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Oncol 2003;21:3431–9. - PubMed
-
- Ng AK, Bernardo MP, Weller E, et al. Long-term survival and competing causes of death in patients with early-stage Hodgkin's disease treated at age 50 or younger. J Clin Oncol 2002;20:2101–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

