Comparison between ultrasound-guided interfascial pulsed radiofrequency and ultrasound-guided interfascial block with local anesthetic in myofascial pain syndrome of trapezius muscle
- PMID: 28151904
- PMCID: PMC5293467
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006019
Comparison between ultrasound-guided interfascial pulsed radiofrequency and ultrasound-guided interfascial block with local anesthetic in myofascial pain syndrome of trapezius muscle
Abstract
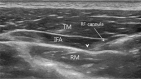
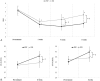
Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) of the trapezius muscle (TM) is a frequently occurring musculoskeletal disorder. However, the treatment of MPS of the TM remains a challenge. We investigated the effects of ultrasound (US)-guided pulsed radiofrequency (PRF) stimulation on the interfascial area of the TM. In addition, we compared its effect with that of interfascial block (IFB) with 10 mL of 0.6% lidocaine on the interfascial area of the TM. Thirty-six patients with MPS of the TM were included and randomly assigned into 2 groups. Eighteen patients underwent PRF stimulation on the interfascial area of the TM (PRF group) and 18 patients underwent IFB with lidocaine on the same area (IFB group). Pain intensity was evaluated using a numerical rating scale (NRS) at pretreatment, 2, 4, and 8 weeks after treatment. At pretreatment and 8 weeks after treatment, quality of life was assessed using the Short Form-36 Health Survey (SF-36), which includes the physical component score (PCS) and the mental component score (MCS). One patient in the PRF group was lost to follow-up. Patients in both groups showed a significant decrease in NRS scores at 2, 4, and 8 weeks after treatments and a significant increase in PCS and MCS of the SF-36 at 8 weeks after treatments. Two weeks after each treatment, the decrements of NRS scores were not significantly different between the 2 groups. However, 4 and 8 weeks after the procedures, we found that the NRS score was significantly lower in the PRF group than in the IFB group. At 8 weeks after the treatments, PCS and MCS of the SF-36 in the PRF group were significantly higher than those in the IFB group. For the management of MPS of the TM, US-guided interfascial PRF had a better long-term effect on reducing the pain and the quality of life compared to US-guided IFB. Therefore, we think US-guided PRF stimulation on the interfascial area of the TM can be a beneficial alternative to manage the pain following MPS of the TM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the Effects of Ultrasound-Guided Interfascial Pulsed Radiofrequency and Ultrasound-Guided Interfascial Injection on Myofascial Pain Syndrome of the Gastrocnemius.Ann Rehabil Med. 2016 Oct;40(5):885-892. doi: 10.5535/arm.2016.40.5.885. Epub 2016 Oct 31. Ann Rehabil Med. 2016. PMID: 27847719 Free PMC article.
-
Results of ultrasound-guided interfascial block of the trapezius muscle for myofascial pain.Agri. 2022 Jul;34(3):187-192. doi: 10.14744/agri.2021.98048. Agri. 2022. PMID: 35792700 English.
-
Effectiveness of Combination of Ultrasonography-Guided Pulsed Radiofrequency Neuromodulation With Steroid at the Suprascapular Nerve in Chronic Shoulder Pain.Pain Pract. 2020 Jan;20(1):16-23. doi: 10.1111/papr.12820. Epub 2019 Aug 24. Pain Pract. 2020. PMID: 31310702 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment and management of myofascial pain syndrome.Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2020 Sep;34(3):427-448. doi: 10.1016/j.bpa.2020.08.003. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2020. PMID: 33004157 Review.
-
Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures: Myofascial Trigger Points With Structured Literature Review.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2017 May/Jun;42(3):407-412. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000572. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2017. PMID: 28277418 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound-guided caudal epidural pulsed radiofrequency for the treatment of failed back surgery syndrome: Results of a prospective clinical study.Interv Pain Med. 2022 Sep 15;1(4):100145. doi: 10.1016/j.inpm.2022.100145. eCollection 2022 Dec. Interv Pain Med. 2022. PMID: 39238870 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomical landmarks and procedure technique of Levator Scapulae Plane Block (LeSP block): Case report: Ultrasound-guided block of the superficial, deep and distal planes of the levator scapulae muscle for treatment of shoulder girdle myofascial pain.Radiol Case Rep. 2024 Sep 26;19(12):6502-6508. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2024.09.050. eCollection 2024 Dec. Radiol Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39380804 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial for the special issue of the Chinese Association for the Study of Pain.World J Clin Cases. 2021 Mar 26;9(9):2022-2026. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i9.2022. World J Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 33850921 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of pulsed radiofrequency on the medial cervical branches for cervical facet joint pain.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Aug 6;10(22):7720-7727. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i22.7720. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 36158472 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of intradiscal pulsed radiofrequency on refractory chronic discogenic neck pain: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Apr;97(16):e0509. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010509. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29668635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robert D, Gerwin Classification, epidemiology, and natural history of myofascial pain syndrome. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2001;5:412–20. - PubMed
-
- Kamanli A, Kaya A, Ardicoglu O. Comparison of lidocaine injection, botulinum toxin injection, and dry needling to trigger points in myofascial pain syndrome. Rheumatol Int 2005;25:604–11. - PubMed
-
- Domingo T, Blasi J, Casals M, et al. Is interfascial injection with ultrasound guided puncture useful in treatment of myofascial pain of the trapezius muscle? Clin J Pain 2011;27:297–303. - PubMed
-
- Hong CZ. Lidocaine injection versus dry needling to myofascial trigger point. The importance of the local twitch response. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 1994;73:256–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

