Highly sensitive detection of a HER2 12-base pair duplicated insertion mutation in lung cancer using the Eprobe-PCR method
- PMID: 28152008
- PMCID: PMC5289711
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171225
Highly sensitive detection of a HER2 12-base pair duplicated insertion mutation in lung cancer using the Eprobe-PCR method
Abstract
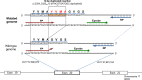
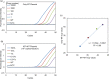
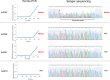
Somatic mutation in human epidermal growth factor receptor-related 2 gene (HER2) is one of the driver mutations in lung cancer. HER2 mutations are found in about 2% of lung adenocarcinomas (ADCs). Previous reports have been based mainly on diagnostic screening by Sanger sequencing or next-generation sequencing (NGS); however, these methods are time-consuming and complicated. We developed a rapid, simple, sensitive mutation detection assay for detecting HER2 12 base pair-duplicated insertion mutation based on the Eprobe-mediated PCR method (Eprobe-PCR) and validated the sensitivity of this assay system for clinical diagnostics. We examined 635 tumor samples and analyzed HER2 mutations using the Eprobe-PCR method, NGS, and Sanger sequencing. In a serial dilution study, the Eprobe-PCR was able to detect mutant plasmid DNA when its concentration was reduced to 0.1% by mixing with wild-type DNA. We also confirmed amplification of the mutated plasmid DNA with only 10 copies per reaction. In ADCs, Eprobe-PCR detected the HER2 mutation in 2.02% (9/446), while Sanger sequencing detected it in 1.57% (7/446). Eprobe-PCR was able to detect the mutation in two samples that were undetectable by Sanger sequencing. All non-ADC samples were wild-type. There were no discrepancies between frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues in the nine samples. HER2 mutations detected by NGS data validated the high sensitivity of the method. Therefore, this new technique can lead to precise molecular-targeted therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
We have the following interests: YK is an inventor of Japanese Patent Application 2012-158229 (”Nucleic acid probe, design method of nucleic acid probe, and detection method for target sequence”, WO 2014/013954 A1). Tatsuo Ichihara (TI) and Yasumasa Mitani (YM) are employed by K.K. DNAFORM. There are no further patents, products in development or marketed products to declare. This does not alter the authors' adherence to all the PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eprobe-mediated screening system for somatic mutations in the KRAS locus.Oncol Rep. 2015 Jun;33(6):2719-27. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3883. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25823645 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a New qPCR-Based System for Screening Mutation.Small. 2019 Mar;15(9):e1805285. doi: 10.1002/smll.201805285. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Small. 2019. PMID: 30677225
-
[Screening for K-ras mutations in colorectal and lung cancers by using a novel real-time PCR with ADx-K-ras kit and Sanger DNA sequencing].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2010 Nov;39(11):757-61. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21215167 Chinese.
-
Performance validation of an amplicon-based targeted next-generation sequencing assay and mutation profiling of 648 Chinese colorectal cancer patients.Virchows Arch. 2018 Jun;472(6):959-968. doi: 10.1007/s00428-018-2359-4. Epub 2018 Apr 28. Virchows Arch. 2018. PMID: 29705968
-
Next‑generation sequencing‑based detection of EGFR, KRAS, BRAF, NRAS, PIK3CA, Her‑2 and TP53 mutations in patients with non‑small cell lung cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Aug;18(2):2191-2197. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9210. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29956783 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Targeted therapy for leptomeningeal metastases in non-small cell lung cancer - Changing treatment paradigms.Chin J Cancer Res. 2017 Dec;29(6):535-542. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2017.06.08. Chin J Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29353976 Free PMC article.
-
CLDN1 Increases Drug Resistance of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Activating Autophagy via Up-Regulation of ULK1 Phosphorylation.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Jun 14;23:2906-2916. doi: 10.12659/msm.904177. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28614291 Free PMC article.
-
Supporting Biomarker-Driven Therapies in Oncology: A Genomic Testing Cost Calculator.Oncologist. 2023 May 8;28(5):e242-e253. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad005. Oncologist. 2023. PMID: 36961477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maemondo M, Minegishi Y, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Harada M, Okinaga S, et al. First-line gefitinib in patients aged 75 or older with advanced non-small cell lung cancer harboring epidermal growth factor receptor mutations: NEJ 003 study. J Thorac Oncol. 2012;7: 1417–1422. 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318260de8b - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arcila ME, Chaft JE, Nafa K, Roy-Chowdhuri S, Lau C, Zaidinski M, et al. Prevalence, Clinicopathologic Associations, and Molecular Spectrum of ERBB2 (HER2) Tyrosine Kinase Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinomas. Clinical Cancer Research. 2012;18: 4910–4918. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0912 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

