Highly tumorigenic hepatocellular carcinoma cell line with cancer stem cell-like properties
- PMID: 28152020
- PMCID: PMC5289561
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171215
Highly tumorigenic hepatocellular carcinoma cell line with cancer stem cell-like properties
Abstract
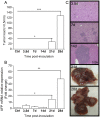
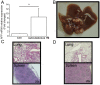
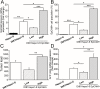
There are limited numbers of models to study hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in vivo in immunocompetent hosts. In an effort to develop a cell line with improved tumorigenicity, we derived a new cell line from Hepa1-6 cells through an in vivo passage in C57BL/6 mice. The resulting Dt81Hepa1-6 cell line showed enhanced tumorigenicity compared to Hepa1-6 with more frequent (28±12 vs. 0±0 lesions at 21 days) and more rapid tumor development (21 (100%) vs. 70 days (10%)) in C57BL/6 mice. The minimal Dt81Hepa1-6 cell number required to obtain visible tumors was 100,000 cells. The Dt81Hepa1-6 cell line showed high hepatotropism with subcutaneous injection leading to liver tumors without development of tumors in lungs or spleen. In vitro, Dt81Hepa1-6 cells showed increased anchorage-independent growth (34.7±6.8 vs. 12.3±3.3 colonies; P<0.05) and increased EpCAM (8.7±1.1 folds; P<0.01) and β-catenin (5.4±1.0 folds; P<0.01) expression. A significant proportion of Dt81Hepa1-6 cells expressed EpCAM compared to Hepa1-6 (34.8±1.1% vs 0.9±0.13%; P<0.001). Enriched EpCAM+ Dt81Hepa1-6 cells led to higher tumor load than EpCAM- Dt81Hepa1-6 cells (1093±74 vs 473±100 tumors; P<0.01). The in vivo selected Dt81Hepa1-6 cell line shows high liver specificity and increased tumorigenicity compared to Hepa1-6 cells. These properties are associated with increased expression of EpCAM and β-catenin confirming that EpCAM+ HCC cells comprise a subset with characteristics of tumor-initiating cells with stem/progenitor cell features. The Dt81Hepa1-6 cell line with its cancer stem cell-like properties will be a useful tool for the study of hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The Novartis/Canadian Liver Foundation Hepatology Research Chair at the Université de Montréal is a philanthropic chair administered by Université de Montréal that was initially founded through a joint initiative of the Canadian Liver Foundation and Novartis to help promote research in the field of liver disease. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products to declare. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

