A putative multi-replicon plasmid co-harboring beta-lactamase genes blaKPC-2, blaCTX-M-14 and blaTEM-1 and trimethoprim resistance gene dfrA25 from a Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type (ST) 11 strain in China
- PMID: 28152085
- PMCID: PMC5289562
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171339
A putative multi-replicon plasmid co-harboring beta-lactamase genes blaKPC-2, blaCTX-M-14 and blaTEM-1 and trimethoprim resistance gene dfrA25 from a Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type (ST) 11 strain in China
Abstract
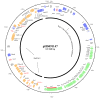
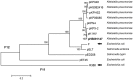
The global emergence of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae poses a major public health threat requiring immediate and aggressive action. Some older generation antibiotics, such as trimethoprim, serve as alternatives for treatment of infections. Here, we determined the complete nucleotide sequence of plasmid pHS091147, which co-harbored the carbapenemase (blaKPC-2) and trimethoprim resistance genes (dfrA25) from a Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type (ST) 11 clone recovered in Shanghai, China. pHS091147 had three replication genes, several plasmid-stability genes and an intact type IV secretion system gene cluster. Besides blaKPC-2 and dfrA25, pHS091147 carried several other resistance genes, including β-lactamase genes blaTEM-1 and blaCTX-M-14, sulphonamide resistance gene sul1, a quinolone resistance gene remnant (ΔqnrB2), and virulence associated gene iroN. Notably, the multidrug-resistance region was a chimeric structure composed of three subregions, which shared strong sequence homology with several plasmids previously assigned in Genbank. To our knowledge, this is the first report of the co-localization of blaKPC-2 and dfrA25 on a novel putative multi-replicon plasmid in a Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 clone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Virulence and transferability of resistance determinants in a novel Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 1137 in China.Microb Drug Resist. 2014 Apr;20(2):150-5. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2013.0107. Epub 2013 Nov 16. Microb Drug Resist. 2014. PMID: 24236613
-
Complete Sequence of a Novel IncR-F33:A-:B- Plasmid, pKP1034, Harboring fosA3, blaKPC-2, blaCTX-M-65, blaSHV-12, and rmtB from an Epidemic Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 11 Strain in China.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Dec 14;60(3):1343-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01488-15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26666939 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Carrying Plasmids in Clinical Isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae from Taiwan.Microb Drug Resist. 2017 Jan;23(1):98-106. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2015.0212. Epub 2016 May 5. Microb Drug Resist. 2017. PMID: 27148814
-
Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, a Key Pathogen Set for Global Nosocomial Dominance.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Oct;59(10):5873-84. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01019-15. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26169401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Klebsiella pneumoniae: a major worldwide source and shuttle for antibiotic resistance.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2017 May 1;41(3):252-275. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fux013. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28521338 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial and the Resistances in the Environment: Ecological and Health Risks, Influencing Factors, and Mitigation Strategies.Toxics. 2023 Feb 16;11(2):185. doi: 10.3390/toxics11020185. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 36851059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of ColE1-like plasmids across γ-Proteobacteria: From bacteriocin production to antimicrobial resistance.PLoS Genet. 2021 Nov 30;17(11):e1009919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009919. eCollection 2021 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34847155 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Genetic Elements Carrying mcr-1 Gene in Escherichia coli from the Community and Hospital Settings in Vietnam.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0135621. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01356-21. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35138158 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization of Carbapenem-Resistant Serratia marcescens Clinical Isolates in a Tertiary Hospital in Hangzhou, China.Infect Drug Resist. 2020 Apr 7;13:999-1008. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S243197. eCollection 2020. Infect Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 32308441 Free PMC article.
-
Trimethoprim and other nonclassical antifolates an excellent template for searching modifications of dihydrofolate reductase enzyme inhibitors.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2020 Jan;73(1):5-27. doi: 10.1038/s41429-019-0240-6. Epub 2019 Oct 2. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2020. PMID: 31578455 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wilkowski P, Ciszek M, Dobrzaniecka K, Sanko-Resmer J, Labus A, Grygiel K, et al. Successful treatment of urinary tract infection in kidney transplant recipients caused by multiresistant Klebsiella pneumoniae producing New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase (NDM-1) with strains genotyping. Transplant Proc. 2016;48(5):1576–9. 10.1016/j.transproceed.2016.01.060 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

