Anthelmintic Potential of Thymoquinone and Curcumin on Fasciola gigantica
- PMID: 28152102
- PMCID: PMC5289557
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171267
Anthelmintic Potential of Thymoquinone and Curcumin on Fasciola gigantica
Abstract
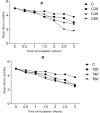
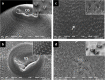
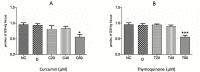
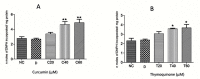
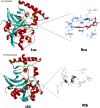
Fasciolosis an economically important global disease of ruminants in the temperate and tropical regions, caused by Fasciola hepatica and F. gigantica, respectively, also poses a potential zoonotic threat. In India alone it causes huge losses to stakeholders. Anthelmintics including triclabendazole have been used to control this menace but the emerging resistance against the available compounds necessitates identification of novel and alternative therapeutic measures involving plant derived natural compounds for their anthelmintic potential. Thymoquinone (T) and curcumin (C), the active ingredients of Nigella sativa and Curcuma longa respectively have been used as antiparasitic agents but the information on their flukicidal effect is very limited. Adult flukes of F. gigantica were in vitro exposed to different concentrations of thymoquinone and curcumin separately for 3h at 37+ 1°C. A significant (p<0.05) reduction in the worm motility at 60 μM concentration of both T and C was observed though all the worms remained alive after 3h exposure, whereas the effect on egg shedding was statistically insignificant. Pronounced tegumental disruptions and erosion of spines in the posterior region and around the acetabulum was evident. A significant (p<0.05) decrease in glutathione-S-transferase and superoxide dismutase activity and reduced glutathione (GSH) level was observed, while protein carbonylation increased differentially. A significant inhibition of CathepsinL (CatL) gene expression in thymoquinone treated worms was also evident. Further, in silico molecular docking of T and C with CatL revealed a stronger interaction of curcumin with the involvement of higher number of amino acids as compared to thymoquinone that could be more effective in inhibiting the antioxidant enzymes of F. gigantica. It is concluded that both the compounds understudy will decrease the detoxification ability of F. gigantica, while inhibition of CatL will significantly affect their virulence potential. Thus, both thymoquinone and curcumin appeared to be promising anthelmintic compounds for further investigations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Mehlhorn H. Encyclopedia of Parasitology Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: 2008. (3rd ed.)
-
- Spithill TW, Smooker PM, Copeman DB. Fasciola gigantica: epidemiology, control, immunology and molecular biology In: Dalton J.P. (Ed.), 1999. Fasciolosis. CABI Publishing, Oxon, UK, (Chapter 15), pp 465–525.
-
- Mas-Coma S. Human fascioliasis 2004; pp 305–322. In Cotruvo J A, Dufour A, Rees G, Bartram J, Carr R, Cliver DO, Craun G F, Fayer R., Gannon VPJ. (Eds.) Waterborne zoonoses: identification, causes and control. World Health Organization (WHO) London, IWA Publishing.
-
- Bhambal SS, Bhandari NR, Bajpai R. Liver-fluke infestation (Fasciola hepatica). Indian Pediatrics, 1980; 17, 469–471. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

