PKCθ-Mediated PDK1 Phosphorylation Enhances T Cell Activation by Increasing PDK1 Stability
- PMID: 28152304
- PMCID: PMC5303887
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2017.2236
PKCθ-Mediated PDK1 Phosphorylation Enhances T Cell Activation by Increasing PDK1 Stability
Abstract
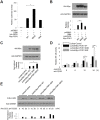
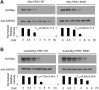
PDK1 is essential for T cell receptor (TCR)-mediated activation of NF-κB, and PDK1-induced phosphorylation of PKCθ is important for TCR-induced NF-κB activation. However, inverse regulation of PDK1 by PKCθ during T cell activation has not been investigated. In this study, we found that PKCθ is involved in human PDK1 phosphorylation and that its kinase activity is crucial for human PDK1 phosphorylation. Mass spectrometry analysis of wild-type PKCθ or of kinase-inactive form of PKCθ revealed that PKCθ induced phosphorylation of human PDK1 at Ser-64. This PKCθ-induced PDK1 phosphorylation positively regulated T cell activation and TCR-induced NF-κB activation. Moreover, phosphorylation of human PDK1 at Ser-64 increased the stability of human PDK1 protein. These results suggest that Ser-64 is an important phosphorylation site that is part of a positive feedback loop for human PDK1-PKCθ-mediated T cell activation.
Keywords: PDK1; PKCθ; T cell; phosphorylation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transition from heterotypic to homotypic PDK1 homodimerization is essential for TCR-mediated NF-κB activation.J Immunol. 2013 May 1;190(9):4508-15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202923. Epub 2013 Mar 25. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23530144 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase Calpha (PKCalpha) acts upstream of PKCtheta to activate IkappaB kinase and NF-kappaB in T lymphocytes.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Oct;23(19):7068-81. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.19.7068-7081.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12972622 Free PMC article.
-
PDK1 nucleates T cell receptor-induced signaling complex for NF-kappaB activation.Science. 2005 Apr 1;308(5718):114-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1107107. Science. 2005. PMID: 15802604
-
Protein kinase C theta (PKCtheta): a key player in T cell life and death.Pharmacol Res. 2007 Jun;55(6):537-44. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2007.04.009. Epub 2007 May 1. Pharmacol Res. 2007. PMID: 17544292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-kappaB activation pathways induced by T cell costimulation.FASEB J. 2003 Dec;17(15):2187-93. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-1100rev. FASEB J. 2003. PMID: 14656980 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent insights of T cell receptor-mediated signaling pathways for T cell activation and development.Exp Mol Med. 2020 May;52(5):750-761. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-0435-8. Epub 2020 May 21. Exp Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32439954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid deletion of phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 enhances NK cell-mediated antitumor immunity by mediating macrophage polarization.Oncoimmunology. 2020 Jun 3;9(1):1774281. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1774281. Oncoimmunology. 2020. PMID: 32923133 Free PMC article.
-
T-helper cells flexibility: the possibility of reprogramming T cells fate.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 1;14:1284178. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1284178. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bi-directional metabolic reprogramming between cancer cells and T cells reshapes the anti-tumor immune response.PLoS Biol. 2025 Jul 14;23(7):e3003284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3003284. eCollection 2025 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2025. PMID: 40658684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balendran A., Biondi R.M., Cheung P.C., Casamayor A., Deak M., Alessi D.R. A 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) docking site is required for the phosphorylation of protein kinase Czeta (PKCzeta ) and PKC-related kinase 2 by PDK1. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:20806–20813. - PubMed
-
- Cho J.E., Kim Y.S., Park S., Cho S.N., Lee H. Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced expression of Leukotactin-1 is mediated by the PI3-K/PDK1/Akt signaling pathway. Mol Cells. 2010;29:35–39. - PubMed
-
- Eckerdt F., Yuan J., Saxena K., Martin B., Kappel S., Lindenau C., Kramer A., Naumann S., Daum S., Fischer G., et al. Polo-like kinase 1-mediated phosphorylation stabilizes Pin1 by inhibiting its ubiquitination in human cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:36575–36583. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

