Musculoskeletal disorders as underlying cause of death in 58 countries, 1986-2011: trend analysis of WHO mortality database
- PMID: 28153007
- PMCID: PMC5290674
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-017-1428-1
Musculoskeletal disorders as underlying cause of death in 58 countries, 1986-2011: trend analysis of WHO mortality database
Abstract
Background: Due to low mortality rate of musculoskeletal disorders (MSK) less attention has been paid to MSK as underlying cause of death in the general population. The aim was to examine trend in MSK as underlying cause of death in 58 countries across globe during 1986-2011.
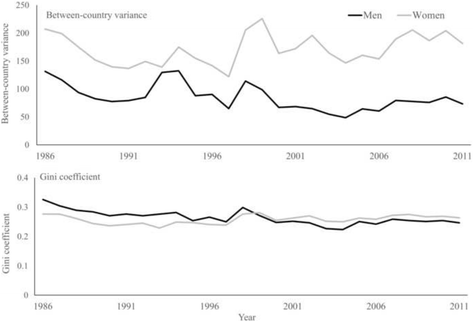
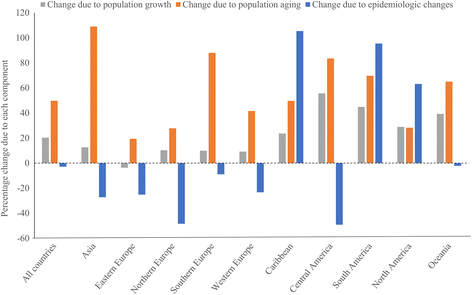
Methods: Data on mortality were collected from the WHO mortality database and population data were obtained from the United Nations. Annual sex-specific age-standardized mortality rates (ASMR) were calculated by means of direct standardization using the WHO world standard population. We applied joinpoint regression analysis for trend analysis. Between-country disparities were examined using between-country variance and Gini coefficient. The changes in number of MSK deaths between 1986 and 2011 were decomposed using two counterfactual scenarios.
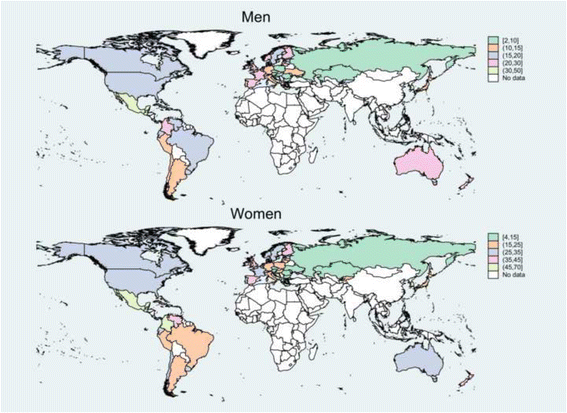
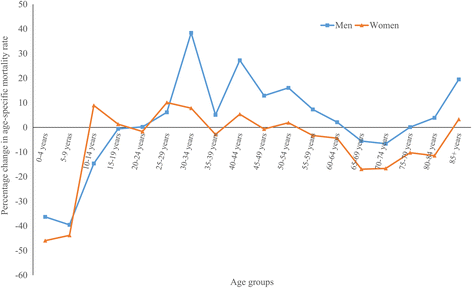
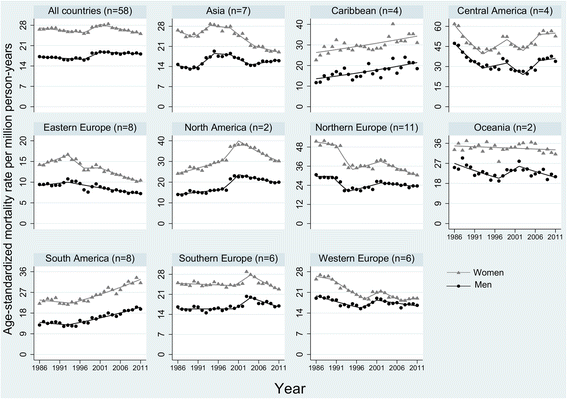
Results: The number of MSK deaths increased by 67% between 1986 and 2011 mainly due to population aging. The mean ASMR changed from 17.2 and 26.6 per million in 1986 to 18.1 and 25.1 in 2011 among men and women, respectively (median: 7.3% increase in men and 9.0% reduction in women). Declines in ASMR of 25% or more were observed for men (women) in 13 (19) countries, while corresponding increases were seen for men (women) in 25 (14) countries. In both sexes, ASMR declined during 1986-1997, then increased during 1997-2001 and again declined over 2001-2011. Despite decline over time, there were substantial between-country disparities in MSK mortality and its temporal trend.
Conclusions: We found substantial variations in MSK mortality and its trends between countries, regions and also between sex and age groups. Promoted awareness and better management of MSK might partly explain reduction in MSK mortality, but variations across countries warrant further investigations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brief Report: Rheumatoid Arthritis as the Underlying Cause of Death in Thirty-One Countries, 1987-2011: Trend Analysis of World Health Organization Mortality Database.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Aug;69(8):1560-1565. doi: 10.1002/art.40091. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28425170
-
Mortality with musculoskeletal disorders as underlying cause in Sweden 1997-2013: a time trend aggregate level study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016 Apr 14;17:163. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-1024-9. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016. PMID: 27075669 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality from Musculoskeletal Disorders Including Rheumatoid Arthritis in Southern Sweden: A Multiple-cause-of-death Analysis, 1998-2014.J Rheumatol. 2017 May;44(5):571-579. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.161219. Epub 2017 Mar 1. J Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28250137
-
Global burden of hypoglycaemia-related mortality in 109 countries, from 2000 to 2014: an analysis of death certificates.Diabetologia. 2018 Jul;61(7):1592-1602. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4626-y. Epub 2018 May 1. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 29717336 Free PMC article.
-
Educational inequalities in mortality associated with rheumatoid arthritis and other musculoskeletal disorders in Sweden.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019 Feb 18;20(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12891-019-2465-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019. PMID: 30777043 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
What is the current evidence of the impact on quality of life whilst waiting for management/treatment of orthopaedic/musculoskeletal complaints? A systematic scoping review.Qual Life Res. 2018 Sep;27(9):2227-2242. doi: 10.1007/s11136-018-1846-z. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Qual Life Res. 2018. PMID: 29611148
-
Population ageing and mortality during 1990-2017: A global decomposition analysis.PLoS Med. 2020 Jun 8;17(6):e1003138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003138. eCollection 2020 Jun. PLoS Med. 2020. PMID: 32511229 Free PMC article.
-
Over-the-Counter Anti-inflammatory Supplements for Adjunctive Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy: A Comprehensive Narrative Review.Aging Dis. 2024 Feb 3;16(1):408-22. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.0131. Online ahead of print. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 38377032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Work-related musculoskeletal disorders among desludging operators in Uganda.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Jun 13;25(1):461. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07564-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38872154 Free PMC article.
-
Rheumatology in Ukraine.Rheumatol Int. 2020 Feb;40(2):175-182. doi: 10.1007/s00296-019-04504-4. Epub 2020 Jan 2. Rheumatol Int. 2020. PMID: 31898762 Review.
References
-
- GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388(10053):1545–602. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- GBD 2015 DALYs and HALE Collaborators Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 315 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE), 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388(10053):1603–58. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31460-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

