Oncogenic signaling of MEK5-ERK5
- PMID: 28153789
- PMCID: PMC5901897
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.01.034
Oncogenic signaling of MEK5-ERK5
Abstract
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) regulate diverse cellular processes including proliferation, cell survival, differentiation, and apoptosis. While conventional MAPK constituents have well-defined roles in oncogenesis, the MEK5 pathway has only recently emerged in cancer research. In this review, we consider the MEK5 signaling cascade, focusing specifically on its involvement in drug resistance and regulation of aggressive cancer phenotypes. Moreover, we explore the role of MEK5/ERK5 in tumorigenesis and metastatic progression, discussing the discrepancies in preclinical studies and assessing its viability as a therapeutic target for anti-cancer agents.
Keywords: Cellular signaling; Kinase inhibitors; MEK5-ERK5; Mitogen-activated protein kinase; Targeted therapies.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
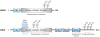

References
-
- Buschbeck M, et al. Phosphotyrosine-specific phosphatase PTP-SL regulates the ERK5 signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(33):29503–9. - PubMed
-
- Cavanaugh JE, et al. Neuroprotective role of ERK1/2 and ERK5 in a dopaminergic cell line under basal conditions and in response to oxidative stress. J Neurosci Res. 2006;84(6):1367–75. - PubMed
-
- Pearson G, et al. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev. 2001;22(2):153–83. - PubMed
-
- English JM, et al. Isolation of MEK5 and differential expression of alternatively spliced forms. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(48):28897–902. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

