Benign Enhancing Foramen Magnum Lesions: Clinical Report of a Newly Recognized Entity
- PMID: 28154124
- PMCID: PMC7960232
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A5085
Benign Enhancing Foramen Magnum Lesions: Clinical Report of a Newly Recognized Entity
Abstract
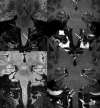
Intradural extramedullary foramen magnum enhancing lesions may be due to meningioma, nerve sheath tumor, aneurysm, or meningeal disease. In this clinical report of 14 patients, we describe a novel imaging finding within the foramen magnum that simulates disease. The lesion is hyperintense on 3D-FLAIR and enhances on 3D gradient-echo sequences but is not seen on 2D-TSE T2WI. It occurs at a characteristic location related to the posterior aspect of the intradural vertebral artery just distal to the dural penetration. Stability of this lesion was demonstrated in those patients who underwent follow-up imaging. Recognition of this apparently benign lesion may prevent unnecessary patient anxiety and repeat imaging.
© 2017 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures




Comment in
-
Imaging Findings of Benign Enhancing Foramen Magnum Lesions.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017 Nov;38(11):E95-E96. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A5330. Epub 2017 Jul 20. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017. PMID: 28729295 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Samii M, Gerganov VM. Surgery of extra-axial tumor of the cerebral base. Neurosurgery 2008;62:1153–66; discussion 1166–68 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
