CD44 Transmembrane Receptor and Hyaluronan Regulate Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem Cell Quiescence and Differentiation
- PMID: 28154169
- PMCID: PMC5377763
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.774109
CD44 Transmembrane Receptor and Hyaluronan Regulate Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem Cell Quiescence and Differentiation
Abstract
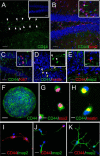
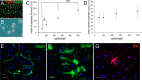
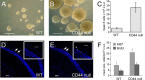
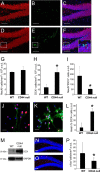
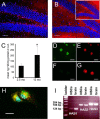
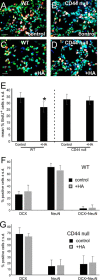
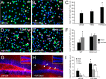
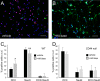
Adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal subgranular zone (SGZ) is involved in learning and memory throughout life but declines with aging. Mice lacking the CD44 transmembrane receptor for the glycosaminoglycan hyaluronan (HA) demonstrate a number of neurological disturbances including hippocampal memory deficits, implicating CD44 in the processes underlying hippocampal memory encoding, storage, or retrieval. Here, we found that HA and CD44 play important roles in regulating adult neurogenesis, and we provide evidence that HA contributes to age-related reductions in neural stem cell (NSC) expansion and differentiation in the hippocampus. CD44-expressing NSCs isolated from the mouse SGZ are self-renewing and capable of differentiating into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. Mice lacking CD44 demonstrate increases in NSC proliferation in the SGZ. This increased proliferation is also observed in NSCs grown in vitro, suggesting that CD44 functions to regulate NSC proliferation in a cell-autonomous manner. HA is synthesized by NSCs and increases in the SGZ with aging. Treating wild type but not CD44-null NSCs with HA inhibits NSC proliferation. HA digestion in wild type NSC cultures or in the SGZ induces increased NSC proliferation, and CD44-null as well as HA-disrupted wild type NSCs demonstrate delayed neuronal differentiation. HA therefore signals through CD44 to regulate NSC quiescence and differentiation, and HA accumulation in the SGZ may contribute to reductions in neurogenesis that are linked to age-related decline in spatial memory.
Keywords: CD44; hippocampus; hyaluronan; neural stem cell (NSC); neurogenesis.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distinct roles for hyaluronan in neural stem cell niches and perineuronal nets.Matrix Biol. 2019 May;78-79:272-283. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.01.022. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Matrix Biol. 2019. PMID: 29408010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein S Regulates Neural Stem Cell Quiescence and Neurogenesis.Stem Cells. 2017 Mar;35(3):679-693. doi: 10.1002/stem.2522. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Stem Cells. 2017. PMID: 27753164
-
Transcription factor NRF2 controls the fate of neural stem cells in the subgranular zone of the hippocampus.Redox Biol. 2017 Oct;13:393-401. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.06.010. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 28667908 Free PMC article.
-
Age-dependent decline in neurogenesis of the hippocampus and extracellular nucleotides.Hum Cell. 2019 Apr;32(2):88-94. doi: 10.1007/s13577-019-00241-9. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Hum Cell. 2019. PMID: 30730038 Review.
-
Grafted Subventricular Zone Neural Stem Cells Display Robust Engraftment and Similar Differentiation Properties and Form New Neurogenic Niches in the Young and Aged Hippocampus.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016 Sep;5(9):1204-15. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0270. Epub 2016 May 18. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27194744 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CD44 mediates hyaluronan to promote the differentiation of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes.Biotechnol Lett. 2023 Mar;45(3):411-422. doi: 10.1007/s10529-022-03322-2. Epub 2023 Jan 21. Biotechnol Lett. 2023. PMID: 36680638
-
Cost-Effective Cosmetic-Grade Hyaluronan Hydrogels for ReNcell VM Human Neural Stem Cell Culture.Biomolecules. 2019 Sep 20;9(10):515. doi: 10.3390/biom9100515. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31547190 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct roles for hyaluronan in neural stem cell niches and perineuronal nets.Matrix Biol. 2019 May;78-79:272-283. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.01.022. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Matrix Biol. 2019. PMID: 29408010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral treatment of 4-methylumbelliferone reduced perineuronal nets and improved recognition memory in mice.Brain Res Bull. 2022 Apr;181:144-156. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.01.011. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Brain Res Bull. 2022. PMID: 35066096 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronan regulates synapse formation and function in developing neural networks.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 5;10(1):16459. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73177-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33020512 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bondolfi L., Ermini F., Long J. M., Ingram D. K., and Jucker M. (2004) Impact of age and caloric restriction on neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of C57BL/6 mice. Neurobiol. Aging 25, 333–340 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

