Transforming Growth Factor-β (TGF-β) Directly Activates the JAK1-STAT3 Axis to Induce Hepatic Fibrosis in Coordination with the SMAD Pathway
- PMID: 28154170
- PMCID: PMC5354477
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.773085
Transforming Growth Factor-β (TGF-β) Directly Activates the JAK1-STAT3 Axis to Induce Hepatic Fibrosis in Coordination with the SMAD Pathway
Abstract
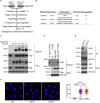
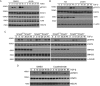
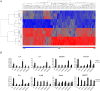
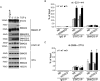
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signals through both SMAD and non-SMAD pathways to elicit a wide array of biological effects. Existing data have shown the association and coordination between STATs and SMADs in mediating TGF-β functions in hepatic cells, but it is not clear how STATs are activated under these circumstances. Here, we report that JAK1 is a constitutive TGFβRI binding protein and is absolutely required for phosphorylation of STATs in a SMAD-independent manner within minutes of TGF-β stimulation. Following the activation of SMADs, TGF-β also induces a second phase of STAT phosphorylation that requires SMADs, de novo protein synthesis, and contribution from JAK1. Our global gene expression profiling indicates that the non-SMAD JAK1/STAT pathway is essential for the expression of a subset of TGF-β target genes in hepatic stellate cells, and the cooperation between the JAK1-STAT3 and SMAD pathways is critical to the roles of TGF-β in liver fibrosis.
Keywords: Janus kinase (JAK); Liver fibrosis; SMAD transcription factor; STAT3; Smad3; hepatic stellate cell (HSC); transforming growth factor beta (TGF-B).
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

References
-
- Fabregat I., Moreno-Càceres J., Sánchez A., Dooley S., Dewidar B., Giannelli G., Ten Dijke P., and IT-LIVER Consortium (2016) TGF-β signalling and liver disease. FEBS J. 283, 2219–2232 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

