Specific Palmitoyltransferases Associate with and Activate the Epithelial Sodium Channel
- PMID: 28154191
- PMCID: PMC5354509
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.776146
Specific Palmitoyltransferases Associate with and Activate the Epithelial Sodium Channel
Abstract
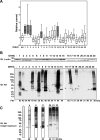
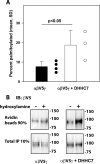
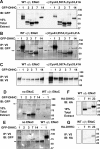
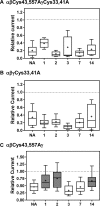
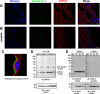
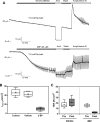
The epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) has an important role in regulating extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure, as well as airway surface liquid volume and mucociliary clearance. ENaC is a trimer of three homologous subunits (α, β, and γ). We previously reported that cytoplasmic residues on the β (βCys-43 and βCys-557) and γ (γCys-33 and γCys-41) subunits are palmitoylated. Mutation of Cys that blocked ENaC palmitoylation also reduced channel open probability. Furthermore, γ subunit palmitoylation had a dominant role over β subunit palmitoylation in regulating ENaC. To determine which palmitoyltransferases (termed DHHCs) regulate the channel, mouse ENaCs were co-expressed in Xenopus oocytes with each of the 23 mouse DHHCs. ENaC activity was significantly increased by DHHCs 1, 2, 3, 7, and 14. ENaC activation by DHHCs was lost when γ subunit palmitoylation sites were mutated, whereas DHHCs 1, 2, and 14 still activated ENaC lacking β subunit palmitoylation sites. β subunit palmitoylation was increased by ENaC co-expression with DHHC 7. Both wild type ENaC and channels lacking β and γ palmitoylation sites co-immunoprecipitated with the five activating DHHCs, suggesting that ENaC forms a complex with multiple DHHCs. RT-PCR revealed that transcripts for the five activating DHHCs were present in cultured mCCDcl1 cells, and DHHC 3 was expressed in aquaporin 2-positive principal cells of mouse aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron where ENaC is localized. Treatment of polarized mCCDcl1 cells with a general inhibitor of palmitoylation reduced ENaC-mediated Na+ currents within minutes. Our results indicate that specific DHHCs have a role in regulating ENaC.
Keywords: Cys palmitoylation; DHHC; epithelial sodium channel (ENaC); ion channel; post-translational modification (PTM); protein acylation; protein palmitoylation.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cysteine palmitoylation of the γ subunit has a dominant role in modulating activity of the epithelial sodium channel.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 16;289(20):14351-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.526020. Epub 2014 Apr 1. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24692558 Free PMC article.
-
Cys palmitoylation of the beta subunit modulates gating of the epithelial sodium channel.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 1;285(40):30453-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.151845. Epub 2010 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20663869 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple palmitoyltransferases are required for palmitoylation-dependent regulation of large conductance calcium- and voltage-activated potassium channels.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 30;285(31):23954-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.137802. Epub 2010 May 27. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20507996 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial Na+ Channel Regulation by Extracellular and Intracellular Factors.Annu Rev Physiol. 2018 Feb 10;80:263-281. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021317-121143. Epub 2017 Nov 9. Annu Rev Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29120692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Roles of DHHC-mediated Protein S-palmitoylation in Physiological and Pathophysiological Context.Eur J Cell Biol. 2018 Jun;97(5):319-338. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2018.03.005. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Eur J Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29602512 Review.
Cited by
-
New insights regarding epithelial Na+ channel regulation and its role in the kidney, immune system and vasculature.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2019 Mar;28(2):113-119. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000479. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2019. PMID: 30585851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β1Pix exchange factor stabilizes the ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-2 and plays a critical role in ENaC regulation by AMPK in kidney epithelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jul 20;293(29):11612-11624. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003082. Epub 2018 Jun 1. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29858246 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between epithelial sodium channels (ENaC) and basolateral potassium channels (Kir 4.1/Kir 5.1) in the cortical collecting duct.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Jun;179(12):2953-2968. doi: 10.1111/bph.15779. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34904226 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating ENaC's gate.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Jan 1;318(1):C150-C162. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00418.2019. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31721612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the vascular endothelial sodium channel activation in the genesis of pathologically increased cardiovascular stiffness.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Jan 7;118(1):130-140. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa326. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 33188592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rossier B. C., and Stutts M. J. (2009) Activation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) by serine proteases. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 71, 361–379 - PubMed
-
- Kellenberger S., and Schild L. (2015) International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology: XCI. structure, function, and pharmacology of acid-sensing ion channels and the epithelial Na+ channel. Pharmacol. Rev. 67, 1–35 - PubMed
-
- Canessa C. M., Merillat A. M., and Rossier B. C. (1994) Membrane topology of the epithelial sodium channel in intact cells. Am. J. Physiol. 267, C1682–C1690 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

