Pathogenesis of Thromboembolism and Endovascular Management
- PMID: 28154761
- PMCID: PMC5244017
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/3039713
Pathogenesis of Thromboembolism and Endovascular Management
Abstract
Venous thromboembolism (VTE), a disease that includes deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), is associated with high mortality, morbidity, and costs. It can result in long-term complications that include postthrombotic syndrome (PTS) adding to its morbidity. VTE affects 1/1000 patients, costs $13.5 billion annually to treat, and claims 100,000 lives annually in the US. The current standard of care for VTE is anticoagulation, though thrombolysis may be performed in patients with PE and threatened limb. This review discusses pathogenesis and medical treatment of VTE and then focuses on endovascular treatment modalities. Mechanical- and catheter-directed thrombolysis (CDT) is discussed, as well as patient selection criteria, and complications. The first prospective study (CaVenT) comparing CDT with anticoagulation alone in acute DVT, despite study shortcomings, corroborates the existing literature indicating improved outcomes with CDT. The potential of the ongoing prospective, multicenter, randomized ATTRACT trial is also highlighted.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests and have no financial disclosures.
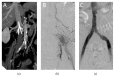
Figures


References
-
- Cohen A. T., Hamilton M., Mitchell S. A., et al. Comparison of the novel oral anticoagulants apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, and rivaroxaban in the initial and long-term treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolism: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(12) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144856.e0144856 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heit J. A., Silverstein M. D., Mohr D. N., Petterson T. M., O'Fallon W. M., Melton L. J., III Predictors of survival after deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a population-based, cohort study. Archives of Internal Medicine. 1999;159(5):445–453. doi: 10.1001/archinte.159.5.445. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
