Morphological relationship analysis of impacted maxillary canines and the adjacent teeth on 3-dimensional reconstructed CT images
- PMID: 28156127
- PMCID: PMC8366694
- DOI: 10.2319/071516-554.1
Morphological relationship analysis of impacted maxillary canines and the adjacent teeth on 3-dimensional reconstructed CT images
Erratum in
-
Errata.Angle Orthod. 2017 Sep;87(5):791. doi: 10.2319/0003-3219-87.5.791. Angle Orthod. 2017. PMID: 28820629 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To examine whether there is a relationship between maxillary canine impaction and the morphologic characteristics of the maxillary dentition, especially the root of the lateral incisor.
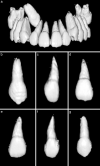
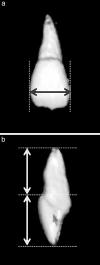
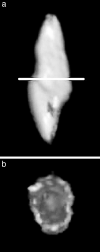
Materials and methods: In this study, we selected only patients with unilateral maxillary canine impaction to compare the morphologic characteristics of the dentition on the impaction side and the clinically normal eruption side. The sample size was decided to be 40 based on the pilot study. To minimize bias depending on sex and location of the maxillary canine impaction, we selected equal numbers (20) of boys and girls, and equal cases (20) of buccal impaction and palatal impaction. Under the aforementioned conditions, the mean age was 13.5 ± 2.3 years. The multislice spiral computed tomography images of these 40 subjects were converted into three-dimensional (3D) reconstructed images using the OnDemand 3D program (Cybermed Co, Seoul, Korea). Then we measured the morphologic characteristics of the individual teeth on the obtained 3D teeth images.
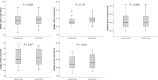
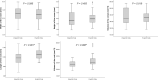
Results: Length and volume of the maxillary lateral incisor's roots were significantly smaller on the impaction side compared with the normal eruption side (P = 0.001 and P = 0.006, respectively). The width and volume of the canine's crown were significantly greater on the impaction side compared with the normal eruption side (P = 0.020 and P < .0001, respectively).
Conclusion: These results might help to prove the hypothesis that the smaller-sized lateral incisor roots and greater-sized canine crowns are the influential etiologic factors in maxillary canine impaction.
Keywords: 3D reconstruction; Guidance theory; Lateral incisor morphology; Maxillary canine impaction.
Figures

References
-
- Andreasen JO, Petersen JK, Laskin DM. Textbook and Color Atlas of Tooth Impactions. Copenhagen, Denmark: Munksgaard; 1997. pp. 126–166.
-
- Becker A. The Orthodontic Treatment of Impacted Teeth 2nd ed. London: Informa Healthcare; 2007. pp. 93–174.
-
- Kung SH, Hwang CJ. Diagnosis and treatment plan of maxillary impacted canine. Korean J Orthod. 1993;23:165–177.
-
- Thilander B, Myrberg N. The prevalence of malocclusion in Swedish school children. Scand J Dent Res. 1973;81:12–21. - PubMed
-
- Ericson S, Kurol J. Radiographic assessment of maxillary canine eruption in children with clinical signs of eruption disturbances. Eur J Orthod. 1986;8:133–140. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

