Passive targeting and lung tolerability of enoxaparin microspheres for a sustained antithrombotic activity in rats
- PMID: 28156170
- PMCID: PMC8241188
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2016.1245368
Passive targeting and lung tolerability of enoxaparin microspheres for a sustained antithrombotic activity in rats
Abstract
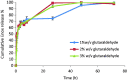
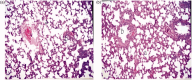
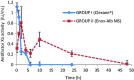
Pulmonary bed can retain microparticles (MP) larger than their capillaries' diameter, hence we offer a promising way for lung passive targeting following intravenous (IV) administration. In this study, enoxaparin (Enox)-albumin microspheres (Enox-Alb MS) were, optimally, developed as lung targeted sustained release MP for IV use. Lung tolerability and targeting efficiency of Enox-Alb MS were tested, and the pharmacokinetic profile following IV administration to albino rats was constructed. In vivo studies confirmed high lung targeting efficiency of Enox-Alb MS with lack of potential tissue toxicity. The anticoagulant activity of the selected Alb MS was significantly sustained for up to 38 h compared to 5 h for the market product. Alb MS are promising delivery carriers for controlled and targeted delivery of Enox to the lungs for prophylaxis and treatment of pulmonary embolism.
Keywords: Albumin; anticoagulant; controlled delivery; enoxaparin; microspheres; passive lung targeting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Polysaccharides-based nanocomplexes for the prolonged delivery of enoxaparin: In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation.Int J Pharm. 2017 Jun 30;526(1-2):271-279. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 May 4. Int J Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28479519
-
A novel point-of-care enoxaparin monitor for use during percutaneous coronary intervention. Results of the Evaluating Enoxaparin Clotting Times (ELECT) Study.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003 Sep 17;42(6):1132-9. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(03)01053-2. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003. PMID: 13678943
-
Safety and effectiveness of enoxaparin following fibrinolytic therapy: Results of the Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI)-QUEBEC registry.Can J Cardiol. 2010 Oct;26(8):431-6. doi: 10.1016/s0828-282x(10)70441-4. Can J Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20931096 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Passive lung-targeted drug delivery systems via intravenous administration.Pharm Dev Technol. 2014 Mar;19(2):129-36. doi: 10.3109/10837450.2012.757782. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Pharm Dev Technol. 2014. PMID: 23336716 Review.
-
Controlled Release Inhalable Polymeric Microspheres for Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(40):5868-76. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666151008124451. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 26446472 Review.
Cited by
-
Construction and Evaluation of Traceable rhES-QDs-M-MS Protein Delivery System: Sustained-Release Properties, Targeted Effect, and Antitumor Activity.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022 Jul 28;23(6):207. doi: 10.1208/s12249-022-02326-5. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022. PMID: 35896916
-
Co-delivery of docetaxel and bortezomib based on a targeting nanoplatform for enhancing cancer chemotherapy effects.Drug Deliv. 2017 Nov;24(1):1124-1138. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2017.1362677. Drug Deliv. 2017. PMID: 28789585 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagre A, Jain K, Jain N. (2013). Alginate coated chitosan core shell nanoparticles for oral delivery of enoxaparin: in vitro and in vivo assessment. Int J Pharm 456:31–40 - PubMed
-
- Bai S, Ahsan F. (2010). Inhalable liposomes of low molecular weight heparin for the treatment of venous thromboembolism. J Pharm Sci 99:4554–64 - PubMed
-
- Bancroft J, Stevens A, Turner D.. 1996. Theory and practice of histological techniques. 4th ed. New York, London, San Francisco, Tokyo: Churchill Livingstone
-
- Boonsongrit Y, Mitrevej A, Mueller B. (2006). Chitosan drug binding by ionic interaction. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 62:267–74 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
