Respiratory syncytial virus infection induces a subset of types I and III interferons in human dendritic cells
- PMID: 28157546
- PMCID: PMC5337151
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2017.01.017
Respiratory syncytial virus infection induces a subset of types I and III interferons in human dendritic cells
Abstract
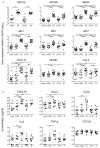
Whether respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) induces severe infantile pulmonary disease may depend on viral strain and expression of types I and III interferons (IFNs). These IFNs impact disease severity by inducing expression of many anti-viral IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs). To investigate the impact of RSV strain on IFN and ISG expression, we stimulated human monocyte-derived DCs (MDDCs) with either RSV A2 or Line 19 and measured expression of types I and III IFNs and ISGs. At 24h, A2 elicited higher ISG expression than Line 19. Both strains induced MDDCs to express genes for IFN-β, IFN-α1, IFN-α8, and IFN-λ1-3, but only A2 induced IFN-α2, -α14 and -α21. We then show that IFN-α8 and IFN-α14 most potently induced MDDCs and bronchial epithelial cells (BECs) to express ISGs. Our findings demonstrate that RSV strain may impact patterns of types I and III IFN expression and the magnitude of the ISG response by DCs and BECs.
Keywords: Bronchial epithelial cell; Dendritic cell; Innate immunity; Interferon; Interferon stimulated gene; Interferon subtype; Respiratory syncytial virus.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Barik S. Respiratory syncytial virus mechanisms to interfere with type 1 interferons. Current topics in microbiology and immunology. 2013;372:173–191. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the royal statistical society. Series B (Methodological) 1995:289–300.
-
- Chanock R, Roizman B, Myers R. Recovery from infants with respiratory illness of a virus related to chimpanzee coryza agent (CCA). I. Isolation, properties and characterization. Am J Hyg. 1957;66:281–290. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

