Neuroprotective effects of dexmedetomidine against hyperoxia-induced injury in the developing rat brain
- PMID: 28158247
- PMCID: PMC5291450
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171498
Neuroprotective effects of dexmedetomidine against hyperoxia-induced injury in the developing rat brain
Abstract
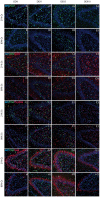
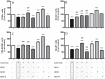
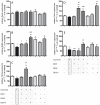
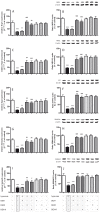
Dexmedetomidine (DEX) is a highly selective agonist of α2-receptors with sedative, anxiolytic, and analgesic properties. Neuroprotective effects of dexmedetomidine have been reported in various brain injury models. In the present study, we investigated the effects of dexmedetomidine on hippocampal neurogenesis, specifically the proliferation capacity and maturation of neurons and neuronal plasticity following the induction of hyperoxia in neonatal rats. Six-day old sex-matched Wistar rats were exposed to 80% oxygen or room air for 24 h and treated with 1, 5 or 10 μg/kg of dexmedetomidine or normal saline. A single pretreatment with DEX attenuated the hyperoxia-induced injury in terms of neurogenesis and plasticity. In detail, both the proliferation capacity (PCNA+ cells) as well as the expression of neuronal markers (Nestin+, PSA-NCAM+, NeuN+ cells) and transcription factors (SOX2, Tbr1/2, Prox1) were significantly reduced under hyperoxia compared to control. Furthermore, regulators of neuronal plasticity (Nrp1, Nrg1, Syp, and Sema3a/f) were also drastically decreased. A single administration of dexmedetomidine prior to oxygen exposure resulted in a significant up-regulation of expression-profiles compared to hyperoxia. Our results suggest that dexmedetomidine may have neuroprotective effects in an acute hyperoxic model of the neonatal rat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effect of dexmedetomidine on hyperoxia-induced toxicity in the neonatal rat brain.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:530371. doi: 10.1155/2015/530371. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 25653737 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine attenuates ethanol-induced inhibition of hippocampal neurogenesis in neonatal mice.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 1;390:114881. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.114881. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31954762
-
Neonatal administration with dexmedetomidine does not impair the rat hippocampal synaptic plasticity later in adulthood.Paediatr Anaesth. 2012 Jul;22(7):713-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2012.03810.x. Epub 2012 Feb 6. Paediatr Anaesth. 2012. PMID: 22309594
-
The potential role of dexmedetomidine on neuroprotection and its possible mechanisms: Evidence from in vitro and in vivo studies.Eur J Neurosci. 2021 Nov;54(9):7006-7047. doi: 10.1111/ejn.15474. Epub 2021 Oct 25. Eur J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34561931 Review.
-
Neuroprotection and neurotoxicity in the developing brain: an update on the effects of dexmedetomidine and xenon.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2017 Mar-Apr;60:102-116. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2017.01.001. Epub 2017 Jan 6. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2017. PMID: 28065636 Review.
Cited by
-
Dexmedetomidine inhibits unstable motor network in patients with primary motor area gliomas.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 May 25;13(11):15139-15150. doi: 10.18632/aging.203077. Epub 2021 May 25. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34032606 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of dexmedetomidine on the expression of inflammatory factors in children with congenital heart disease undergoing intraoperative cardiopulmonary bypass: a randomized controlled trial.Pediatr Investig. 2020 Mar 17;4(1):23-28. doi: 10.1002/ped4.12176. eCollection 2020 Mar. Pediatr Investig. 2020. PMID: 32851338 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Early Caffeine Administration in Hyperoxia-Induced Neurotoxicity in the Juvenile Rat.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 28;12(2):295. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020295. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829854 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on the effects and mechanisms of anesthetics on neural stem cells.Ibrain. 2022 Nov 7;8(4):453-464. doi: 10.1002/ibra.12071. eCollection 2022 Winter. Ibrain. 2022. PMID: 37786590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dexmedetomidine upregulates microRNA-185 to suppress ovarian cancer growth via inhibiting the SOX9/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Cell Cycle. 2021 Apr;20(8):765-780. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1897270. Epub 2021 Apr 4. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 33818283 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perrone S, Tataranno ML, Santacroce A, Negro S, Buonocore G (2014) The role of oxidative stress on necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight infants. Curr Pediatr Rev 10: 202–207. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

