Study protocol; Thyroid hormone Replacement for Untreated older adults with Subclinical hypothyroidism - a randomised placebo controlled Trial (TRUST)
- PMID: 28158982
- PMCID: PMC5291970
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-017-0156-8
Study protocol; Thyroid hormone Replacement for Untreated older adults with Subclinical hypothyroidism - a randomised placebo controlled Trial (TRUST)
Abstract
Background: Subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) is a common condition in elderly people, defined as elevated serum thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) with normal circulating free thyroxine (fT4). Evidence is lacking about the effect of thyroid hormone treatment. We describe the protocol of a large randomised controlled trial (RCT) of Levothyroxine treatment for SCH.
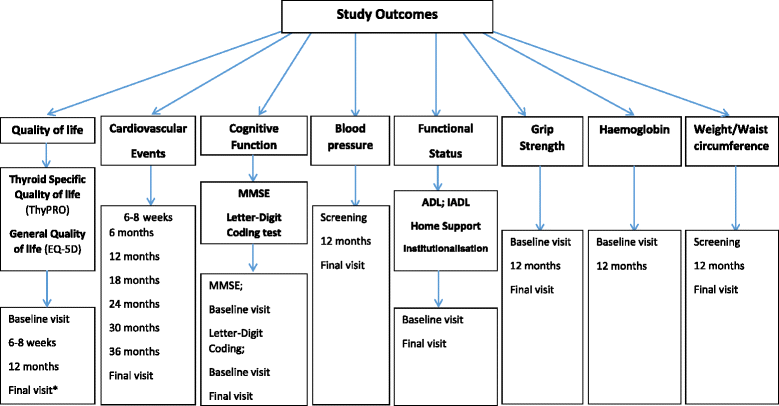
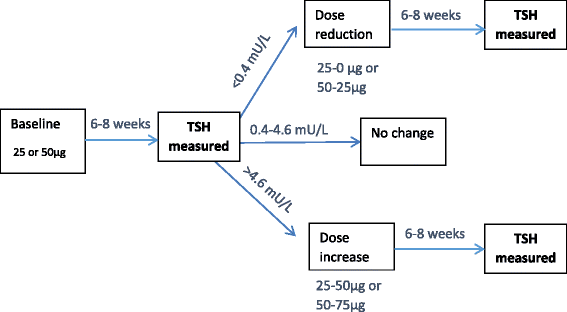
Methods: Participants are community-dwelling subjects aged ≥65 years with SCH, diagnosed by elevated TSH levels (≥4.6 and ≤19.9 mU/L) on a minimum of two measures ≥ three months apart, with fT4 levels within laboratory reference range. The study is a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled parallel group trial, starting with levothyroxine 50 micrograms daily (25 micrograms in subjects <50Kg body weight or known coronary heart disease) with titration of dose in the active treatment group according to TSH level, and a mock titration in the placebo group. The primary outcomes are changes in two domains (hypothyroid symptoms and fatigue / vitality) on the thyroid-related quality of life questionnaire (ThyPRO) at one year. The study has 80% power (at p = 0.025, 2-tailed) to detect a change with levothyroxine treatment of 3.0% on the hypothyroid scale and 4.1% on the fatigue / vitality scale with a total target sample size of 750 patients. Secondary outcomes include general health-related quality of life (EuroQol), fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events, handgrip strength, executive cognitive function (Letter Digit Coding Test), basic and instrumental activities of daily living, haemoglobin, blood pressure, weight, body mass index and waist circumference. Patients are monitored for specific adverse events of interest including incident atrial fibrillation, heart failure and bone fracture.
Discussion: This large multicentre RCT of levothyroxine treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism is powered to detect clinically relevant change in symptoms / quality of life and is likely to be highly influential in guiding treatment of this common condition.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov NCT01660126 ; registered 8th June 2012.
Keywords: Elderly; Levothyroxine; Quality of life; Randomised controlled trial; Subclinical hypothyroidism; Thyroid disease.
Figures
References
-
- Baumgartner C, Blum MR, Rodondi N. Subclinical hypothyroidism: summary of evidence in 2014. Swiss Med Wkly. 2014;144:w14058. - PubMed
-
- Parle J, Roberts L, Wilson S, Pattison H, Roalfe A, Haque MS, et al. A randomized controlled trial of the effect of thyroxine replacement on cognitive function in community-living elderly subjects with subclinical hypothyroidism: the Birmingham Elderly Thyroid study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(8):3623–32. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-2571. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

