Evidence-Based Methods That Promote Human Milk Feeding of Preterm Infants: An Expert Review
- PMID: 28159199
- PMCID: PMC5328421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clp.2016.11.005
Evidence-Based Methods That Promote Human Milk Feeding of Preterm Infants: An Expert Review
Abstract
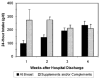
Best practices translating the evidence for high-dose human milk (HM) feeding for preterm infants during neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) hospitalization have been described, but their implementation has been compromised. Although the rates of any HM feeding have increased over the last decade, efforts to help mothers maintain HM provision through to NICU discharge have remained problematic. Special emphasis should be placed on prioritizing the early lactation period of coming to volume so that mothers have sufficient HM volume to achieve their personal HM feeding goals. Donor HM does not provide the same risk reduction as own mother's HM.
Keywords: Breast pump; Human milk; Lactation initiation and maintenance; Neonatal intensive care unit; Preterm infants.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Meier PP, Patel AL, Bigger HR, et al. Human milk feedings in the neonatal intensive care unit. In: Rajendram R, Preedy VR, Patel VB, editors. Diet and nutrition in critical care. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2015. pp. 807–822.
-
- Vohr BR, Poindexter BB, Dusick AM, et al. Beneficial effects of breast milk in the neonatal intensive care unit on the developmental outcome of extremely low birth weight infants at 18 months of age. Pediatrics. 2006;118(1):e115–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

