Multiple functional self-association interfaces in plant TIR domains
- PMID: 28159890
- PMCID: PMC5347627
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1621248114
Multiple functional self-association interfaces in plant TIR domains
Abstract
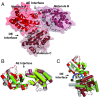
The self-association of Toll/interleukin-1 receptor/resistance protein (TIR) domains has been implicated in signaling in plant and animal immunity receptors. Structure-based studies identified different TIR-domain dimerization interfaces required for signaling of the plant nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors (NLRs) L6 from flax and disease resistance protein RPS4 from Arabidopsis Here we show that the crystal structure of the TIR domain from the Arabidopsis NLR suppressor of npr1-1, constitutive 1 (SNC1) contains both an L6-like interface involving helices αD and αE (DE interface) and an RPS4-like interface involving helices αA and αE (AE interface). Mutations in either the AE- or DE-interface region disrupt cell-death signaling activity of SNC1, L6, and RPS4 TIR domains and full-length L6 and RPS4. Self-association of L6 and RPS4 TIR domains is affected by mutations in either region, whereas only AE-interface mutations affect SNC1 TIR-domain self-association. We further show two similar interfaces in the crystal structure of the TIR domain from the Arabidopsis NLR recognition of Peronospora parasitica 1 (RPP1). These data demonstrate that both the AE and DE self-association interfaces are simultaneously required for self-association and cell-death signaling in diverse plant NLRs.
Keywords: NLR; TIR domain; plant disease resistance; plant immunity; signaling by cooperative assembly formation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Comment in
-
Two-faced TIRs trip the immune switch.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 7;114(10):2445-2446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1700954114. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28242711 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dodds PN, Rathjen JP. Plant immunity: Towards an integrated view of plant-pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11(8):539–548. - PubMed
-
- Duxbury Z, et al. Pathogen perception by NLRs in plants and animals: Parallel worlds. BioEssays. 2016;38(8):769–781. - PubMed
-
- van der Biezen EA, Jones JD. The NB-ARC domain: A novel signalling motif shared by plant resistance gene products and regulators of cell death in animals. Curr Biol. 1998;8(7):R226–R227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

