The impact of BMI on sperm parameters and the metabolite changes of seminal plasma concomitantly
- PMID: 28159940
- PMCID: PMC5564712
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14950
The impact of BMI on sperm parameters and the metabolite changes of seminal plasma concomitantly
Abstract
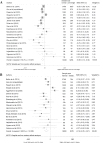
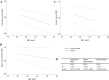
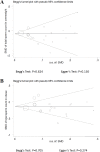
The development of male infertility increased rapidly worldwide, which coinciding with the epidemic of obesity. However, the impact of weight abnormalities on sperm quality is still contestable. To assess the correlation between BMI and sperm parameters, we searched relevant articles in PubMed, Embase, Web of science, and Wanfang database published until June 2015 without language restriction. Otherwise, we also recruited some participants who attended fertility clinic as well as some general populations in this report. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis about BMI and sperm parameters containing total sperm count, concentration, semen volume and sperm motility (overall and progressive). Metabolomic analysis of seminal plasma was performed to explore the mechanism from a new perspective. This study found standardized weighted mean differences (SMD) in sperm parameters (total sperm count, sperm concentration, and semen volume) of abnormal weight groups decreased to different degree compared to normal weight. Dose-response analysis found SMD of sperm count, sperm concentration and semen volume respectively fell 2.4%, 1.3% and 2.0% compared with normal weight for every 5-unit increase in BMI. Metabolomic analysis of seminal plasma showed that spermidine and spermine were likely to play a vital role in the spermatogenesis progress. This systematic review with meta-analysis has confirmed there was a relationship between BMI and sperm quality, suggesting obesity may be a detrimental factor of male infertility.
Keywords: BMI; Pathology Section; meta-analysis; metabolomic analysis; obesity; sperm parameters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Gurunath S, Pandian Z, Anderson RA, Bhattacharya S. Defining infertility—a systematic review of prevalence studies. Hum Reprod Update. 2011;17:575–88. - PubMed
-
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, Mullany EC, Biryukov S, Abbafati C, Abera SF, Abraham JP, Abu-Rmeileh NM, Achoki T, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384:766–81. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

