Shear wave elastography combined with the thyroid imaging reporting and data system for malignancy risk stratification in thyroid nodules
- PMID: 28160573
- PMCID: PMC5522156
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15018
Shear wave elastography combined with the thyroid imaging reporting and data system for malignancy risk stratification in thyroid nodules
Abstract
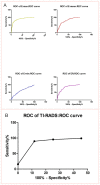
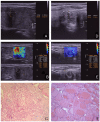
To retrospectively evaluate the diagnostic performance of shear wave elastography (SWE) and thyroid imaging reporting and data system (TI-RADS) in differentiating malignant and benign thyroid nodules. A total of 313 thyroid nodules in 227 patients were included. All thyroid nodules were underwent SWE and TI-RADS before fine needle aspiration biopsy and/or surgery. SWE elasticity indices of the maximum (Emax), mean (Emean), minimum (Emin) and elastic ratio (ER) in thyroid nodules were measured. Nodules with solid component, marked hypoechogenicity, poorly defined margins, micro-calcifications, and a taller-than-wide shape were classified as suspicious at gray-scale ultrasonography. The level of TI-RADS was determined according to the number of suspicious ultrasonography features. The combined methods of SWE and TI-RADS in thyroid nodules were calculated. In the 313 nodules, 194 were malignant, and 119 were benign. SWE and TI-RADS were significantly higher in malignant nodules than benign nodules (P < 0.001). The most accurate SWE cut-off value, 51.95 kPa for Emax, achieved a sensitivity of 81.44% and a specificity of 83.19% for discriminating malignant nodules from benign nodules. There are two methods in combination with SWE and TI-RADS. The one is "tandem" method, which has a higher specificity (95.80%), positive likelihood ratio (18.16) and positive predictive value (96.73%). The other one is "parallel" method, which shows sensitivity (94.85%), negative likelihood ratio (0.07) and negative predictive value (90.00%).We believe that the methods could be used as a simple tool to stratify the risk of thyroid nodules accurately.
Keywords: diagnostic performance; shear wave elastography (SWE); thyroid imaging reporting and data system (TI-RADS); thyroid nodules; “tandem” and “parallel”.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Guth S, Theune U, Aberle J, Galach A, Bamberger CM. Very high prevalence of thyroid nodules detected by high frequency (13 MHz) ultrasound examination. Eur J Clin Invest. 2009(39):699–706. - PubMed
-
- Tan GH, Gharib H. Thyroid incidentalomas: management approaches to nonpalpable nodules discovered incidentally on thyroid imaging. Ann Intern Med. 1997(126):226–231. - PubMed
-
- Kim KW, Kim EK, Kwak JY, Kim MJ. Detection and management of thyroid incidentalomas. J Korean Soc Ultrasound Med. 2008(27):111–117.
-
- Kim MJ, Kim EK, Park SI, Kim BM, Kwak JY, Kim SJ, Youk JH, Park SH. US-guided fine-needle aspiration of thyroid nodules: indications, techniques, results. RadioGraphics. 2008(28):1869–1886. - PubMed
-
- Paschke R, Hegedüs L, Alexander E, Valcavi R, Papini E, Gharib H. Thyroid nodule guidelines: agreement, disagreement and need for future research. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011(7):354–361. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

