Sclerotherapy for the recurrent granulomatous epulis with pingyangmycin
- PMID: 28160580
- PMCID: PMC5359704
- DOI: 10.4317/medoral.21422
Sclerotherapy for the recurrent granulomatous epulis with pingyangmycin
Abstract
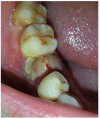
Background: Relapse of granulomatous epulis is common after surgery because of local irritations, hormonal level in vivo, or incomplete resection. Currently, if recurrence occurs, then extraction of the teeth adjacent to the lesion is commonly performed, which may influence the aesthetics or masticatory function. Thus, a more effective and less aggressive treatment method is urgently demanded, particularly for the recurring lesion. This study investigated the effects of the intralesional pingyangmycin (PYM) injections for the recurrent granulomatous epulis and assessed the complications.
Material and methods: A total of 16 patients with recurrent granulomatous epulis underwent intralesional PYM injections, between July 2010 and June 2014. The effects and complications of the treatment were retrospectively reviewed.
Results: The total number of injections performed was 48 (for all patients). The median number of injections per patient was three (range, two to four). All cases completely recovered with no recurrence and resorption of the alveolar bone after a follow-up of more than 12 months. The complications included slight bleeding, local swelling and pain following injection. All these symptoms resolved 7 to 10 days after the injection.
Conclusions: In summary, intralesional PYM injections may be a preferred option for recurring granulomatous epulis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sclerotherapy for the mucoceles of the anterior lingual salivary glands with pingyangmycin.Oral Dis. 2014 Jul;20(5):473-6. doi: 10.1111/odi.12155. Epub 2013 Jul 15. Oral Dis. 2014. PMID: 23848975
-
Intralesional injection of Pingyangmycin may be an effective treatment for epulis.Med Hypotheses. 2009 Apr;72(4):453-4. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2008.10.022. Epub 2009 Jan 7. Med Hypotheses. 2009. PMID: 19131174
-
A clinical study of pingyangmycin sclerotherapy for venous malformation: an evaluation of 281 consecutive patients.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2014 Oct;39(5):521-6. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12183. Epub 2014 Jun 13. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2014. PMID: 24924412 Clinical Trial.
-
Sclerotherapy of microcystic lymphatic malformations in oral and facial regions.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009 Feb;67(2):251-6. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2008.06.046. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009. PMID: 19138596 Clinical Trial.
-
[The clinical and therapeutic aspects of epulis gravidarum].Minerva Stomatol. 1990 Dec;39(12):1023-6. Minerva Stomatol. 1990. PMID: 2092185 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
980-nm diode laser excision of a giant pregnancy epulis.Pak J Med Sci. 2022 Mar-Apr;38(3Part-I):773-775. doi: 10.12669/pjms.38.3.5102. Pak J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35480503 Free PMC article.
-
Sclerotherapy - A novel modality in the management of oral pyogenic granuloma.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2021 Mar-Apr;25(2):162-165. doi: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_189_20. Epub 2021 Mar 1. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2021. PMID: 33888950 Free PMC article.
-
Nd:YAG water mist laser treatment for giant gestational gingival tumor: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Apr 16;12(11):1974-1979. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i11.1974. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 38660558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu C, Qin ZP, Fan ZN, Zhao WJ, Wang YM, Wei FC. New treatment strategy for granulomatous epulis: intralesional injection of propranolol. Med Hypotheses. 2012;78:327–9. - PubMed
-
- Zheng JW, Zhou Q, Yang XJ, He Y, Wang YA, Ye WM. Intralesional injection of Pingyangmycin may be an effective treatment for epulis. Med Hypotheses. 2009;72:453–4. - PubMed
-
- Jafarzadeh H, Sanatkhani M, Mohtasham N. Oral pyogenic granuloma: a review. J Oral Sci. 2006;48:167–75. - PubMed
-
- Al-Khateeb T, Ababneh K. Oral pyogenic granuloma in Jordanians: a retrospective analysis of 108 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;61:1285–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

