1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Ameliorates Seawater Aspiration-Induced Lung Injury By Inhibiting The Translocation Of NF-κB and RhoA
- PMID: 28161733
- PMCID: PMC5429345
- DOI: 10.1007/s10753-017-0527-3
1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Ameliorates Seawater Aspiration-Induced Lung Injury By Inhibiting The Translocation Of NF-κB and RhoA
Abstract
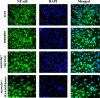
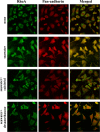
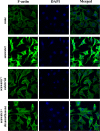
Our previous study have reported that 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol) suppresses seawater aspiration-induced ALI in vitro and in vivo. We also have confirmed that treatment with calcitriol ameliorates seawater aspiration-induced inflammation and pulmonary edema via the inhibition of NF-κB and RhoA/Rho kinase pathway activation. In our further work, we investigated the effect of calcitriol on nuclear translocation of NF-κB and membrane translocation of RhoA in vitro. A549 cells and rat pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (RPMVECs) were cultured with calcitriol or not for 48 h and then stimulated with 25% seawater for 40 min. After these treatments, cells were collected and performed with immunofluorescent staining to observe the translocation of NF-κB and RhoA and the cytoskeleton remodeling. In vitro, seawater stimulation activates nuclear translocation of NF-κB and membrane translocation of RhoA in A549 cells. In addition, seawater administration also induced cytoskeleton remodeling in A549 cells and RPMVECs. However, pretreatment with calcitriol significantly inhibited the activation of NF-κB and RhoA/Rho kinase pathways, as demonstrated by the reduced nuclear translocation of NF-κB and membrane translocation of RhoA in A549 cells. Meanwhile, treatment of calcitriol also regulated the cytoskeleton remodeling in both A549 cells and RPMVECs. These results demonstrated that treatment with calcitriol ameliorates seawater aspiration-induced ALI via inhibition of nuclear translocation of NF-κB and membrane translocation of RhoA and protection of alveolar epithelial and pulmonary microvascular endothelial barrier.
Keywords: 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3; NF-κB; RhoA; acute lung injury; seawater.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 ameliorates seawater aspiration-induced acute lung injury via NF-κB and RhoA/Rho kinase pathways.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 13;9(8):e104507. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104507. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25118599 Free PMC article.
-
The vitamin D receptor agonist elocalcitol inhibits IL-8-dependent benign prostatic hyperplasia stromal cell proliferation and inflammatory response by targeting the RhoA/Rho kinase and NF-kappaB pathways.Prostate. 2009 Apr 1;69(5):480-93. doi: 10.1002/pros.20896. Prostate. 2009. PMID: 19107880
-
Endothelial semaphorin 7A promotes seawater aspiration-induced acute lung injury through plexin C1 and β1 integrin.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Oct;16(4):4215-4221. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7097. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28765893
-
Vitamin D attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting inflammation via suppressing the RhoA/ROCK/NF-ĸB pathway.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2019 Sep;66(5):850-857. doi: 10.1002/bab.1797. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31245891
-
GEF-H1/RhoA signaling pathway mediates pro-inflammatory effects of NF-κB on CD40L-induced pulmonary endothelial cells.Mol Immunol. 2023 May;157:42-52. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2023.03.015. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Mol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36989839
Cited by
-
Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) as a potential therapeutic target for lung diseases: a narrative review.J Thorac Dis. 2024 Nov 30;16(11):8026-8038. doi: 10.21037/jtd-24-734. Epub 2024 Nov 29. J Thorac Dis. 2024. PMID: 39678849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of neurite outgrowth using commercial myelin associated glycoprotein-Fc in neuro-2a cells.Neural Regen Res. 2018 Nov;13(11):1893-1899. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.239438. Neural Regen Res. 2018. PMID: 30233061 Free PMC article.
-
Vaporization of perfluorocarbon attenuates sea-water-drowning-induced acute lung injury by deactivating the NLRP3 inflammasomes in canines.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2024 Apr 19;249:10104. doi: 10.3389/ebm.2024.10104. eCollection 2024. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2024. PMID: 38708425 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Role in Co-Ordinating SARS-CoV-2 Entry and Symptomatology: Linking Cytotoxicity Changes in COVID-19 and Cancers; Modulation by Racial Discrimination Stress.Biology (Basel). 2020 Aug 27;9(9):249. doi: 10.3390/biology9090249. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32867244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D3 improved hypoxia-induced lung injury by inhibiting the complement and coagulation cascade and autophagy pathway.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Jan 2;24(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12890-023-02784-y. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 38166725 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

