Homology-guided mutational analysis reveals the functional requirements for antinociceptive specificity of collapsin response mediator protein 2-derived peptides
- PMID: 28161890
- PMCID: PMC5980424
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13737
Homology-guided mutational analysis reveals the functional requirements for antinociceptive specificity of collapsin response mediator protein 2-derived peptides
Abstract
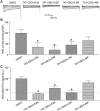
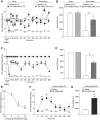
Background and purpose: N-type voltage-gated calcium (Cav 2.2) channels are critical determinants of increased neuronal excitability and neurotransmission accompanying persistent neuropathic pain. Although Cav 2.2 channel antagonists are recommended as first-line treatment for neuropathic pain, calcium-current blocking gabapentinoids inadequately alleviate chronic pain symptoms and often exhibit numerous side effects. Collapsin response mediator protein 2 (CRMP2) targets Cav 2.2 channels to the sensory neuron membrane and allosterically modulates their function. A 15-amino-acid peptide (CBD3), derived from CRMP2, disrupts the functional protein-protein interaction between CRMP2 and Cav 2.2 channels to inhibit calcium influx, transmitter release and acute, inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Here, we have mapped the minimal domain of CBD3 necessary for its antinociceptive potential.
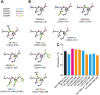
Experimental approach: Truncated as well as homology-guided mutant versions of CBD3 were generated and assessed using depolarization-evoked calcium influx in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons, binding between CRMP2 and Cav 2.2 channels, whole-cell voltage clamp electrophysiology and behavioural effects in two models of experimental pain: post-surgical pain and HIV-induced sensory neuropathy induced by the viral glycoprotein 120.
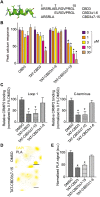
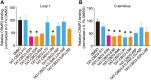
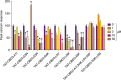
Key results: The first six amino acids within CBD3 accounted for all in vitro activity and antinociception. Spinal administration of a prototypical peptide (TAT-CBD3-L5M) reversed pain behaviours. Homology-guided mutational analyses of these six amino acids identified at least two residues, Ala1 and Arg4, as being critical for antinociception in two pain models.
Conclusions and implications: These results identify an antinociceptive scaffold core in CBD3 that can be used for development of low MW mimetics of CBD3.
Linked articles: This article is part of a themed section on Recent Advances in Targeting Ion Channels to Treat Chronic Pain. To view the other articles in this section visit http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.v175.12/issuetoc.
© 2017 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A membrane-delimited N-myristoylated CRMP2 peptide aptamer inhibits CaV2.2 trafficking and reverses inflammatory and postoperative pain behaviors.Pain. 2015 Jul;156(7):1247-1264. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000147. Pain. 2015. PMID: 25782368 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained relief of ongoing experimental neuropathic pain by a CRMP2 peptide aptamer with low abuse potential.Pain. 2016 Sep;157(9):2124-2140. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000628. Pain. 2016. PMID: 27537210 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained relief of neuropathic pain by AAV-targeted expression of CBD3 peptide in rat dorsal root ganglion.Gene Ther. 2014 Jan;21(1):44-51. doi: 10.1038/gt.2013.56. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Gene Ther. 2014. PMID: 24152582 Free PMC article.
-
Challenging the catechism of therapeutics for chronic neuropathic pain: Targeting CaV2.2 interactions with CRMP2 peptides.Neurosci Lett. 2013 Dec 17;557 Pt A(0 0):27-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.06.057. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Neurosci Lett. 2013. PMID: 23831344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide and Peptidomimetic Inhibitors Targeting the Interaction of Collapsin Response Mediator Protein 2 with the N-Type Calcium Channel for Pain Relief.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Jun 6;7(7):1916-1936. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00181. eCollection 2024 Jul 12. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39022365 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuronal Conditional Knockout of Collapsin Response Mediator Protein 2 Ameliorates Disease Severity in a Mouse Model of Multiple Sclerosis.ASN Neuro. 2019 Jan-Dec;11:1759091419892090. doi: 10.1177/1759091419892090. ASN Neuro. 2019. PMID: 31795726 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of edonerpic maleate as a CRMP2 inhibitor for pain relief.Channels (Austin). 2019 Dec;13(1):498-504. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2019.1684608. Channels (Austin). 2019. PMID: 31680630 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylated CRMP2 Regulates Spinal Nociceptive Neurotransmission.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Jul;56(7):5241-5255. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1445-6. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30565051 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted transcriptional upregulation of SENP1 by CRISPR activation enhances deSUMOylation pathways to elicit antinociception in the spinal nerve ligation model of neuropathic pain.Pain. 2024 Apr 1;165(4):866-883. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003080. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Pain. 2024. PMID: 37862053 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in targeting ion channels to treat chronic pain.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Jun;175(12):2133-2137. doi: 10.1111/bph.14215. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29878335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atanassoff PG, Hartmannsgruber MW, Thrasher J, Wermeling D, Longton W, Gaeta R et al. (2000). Ziconotide, a new N‐type calcium channel blocker, administered intrathecally for acute postoperative pain. Reg Anesth Pain Med 25: 274–278. - PubMed
-
- Attal N, Cruccu G, Baron R, Haanpaa M, Hansson P, Jensen TS et al. (2010). EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. Eur J Neurol 17: 1113–e1188. - PubMed
-
- Backonja M, Woolf CJ (2010). Future directions in neuropathic pain therapy: closing the translational loop. Oncologist 15 (Suppl 2): 24–29. - PubMed
-
- Bauer CS, Rahman W, Tran‐van‐Minh A, Lujan R, Dickenson AH, Dolphin AC (2010). The anti‐allodynic alpha(2)delta ligand pregabalin inhibits the trafficking of the calcium channel alpha(2)delta‐1 subunit to presynaptic terminals in vivo. Biochem Soc Trans 38: 525–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

