Hypertension influences the exponential progression of inflammation and oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic kidney
- PMID: 28163536
- PMCID: PMC5242028
- DOI: 10.4103/0976-500X.195898
Hypertension influences the exponential progression of inflammation and oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic kidney
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the association of hypertension coexisting with diabetes mellitus with oxidative stress and inflammation in the kidneys of streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats.
Materials and methods: Male Wistar rats were used for the experiments. Blood glucose (BG), urea, blood pressure (BP), and heart rate (HR) were analyzed before and 48 h after STZ injection. Further, these parameters were monitored up to 3 months of diabetes induction. Subsequently, the inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and nitrate) and oxidative stress markers were estimated after 3 months of diabetes induction in the kidney homogenate. Histological analysis of renal tissue was also carried out.
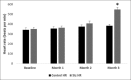
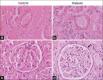
Results: Linear elevation of BG, urea, mean arterial pressure (MAP), and HR was observed up to 3 months of diabetes induction. In the same manner, inflammatory and oxidative stress markers were also found to be significantly increased. Notably, the histological analysis revealed the signs of nephropathy such as increased mesangial cell number, thickness of basement membrane, and renal artery. Inflammatory and oxidative stress markers positively correlated with elevated BP and BG, but the correlation was better with BP rather than BG.
Conclusion: Hypertension has a strong implication in the increased oxidative stress and inflammation of diabetic kidney at the very early stage of diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; diabetic nephropathy; hypertension; streptozotocin and oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Jensen T, Borch-Johnsen K, Deckert T. Changes in blood pressure and renal function in patients with type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus prior to clinical diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Res. 1987;4:159–62. - PubMed
-
- Parving HH. Controlling hypertension in diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2002;39(Suppl 2):S35–40. - PubMed
-
- Tarnow L, Rossing P, Gall MA, Nielsen FS, Parving HH. Prevalence of arterial hypertension in diabetic patients before and after the JNC-V. Diabetes Care. 1994;17:1247–51. - PubMed
-
- Epstein M, Sowers JR. Diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Hypertension. 1992;19:403–18. - PubMed
-
- Cruickshanks KJ, Orchard TJ, Becker DJ. The cardiovascular risk profile of adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1985;8:118–24. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

